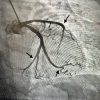
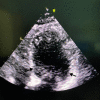
A Broken Heart: A Case of Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 34976528
- PMCID: PMC8712236
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19933
A Broken Heart: A Case of Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Emotional stress-induced left ventricular dysfunction, also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, is a condition that has become more prevalent since the turn of the century. Seen most commonly in postmenopausal women who experience an acute emotional stressor, its presentation resembles that of acute coronary syndrome with electrocardiogram changes, which is why most patients receive a left heart catheterization revealing clean or nonobstructive coronary arteries.
Keywords: broken heart syndrome; reversible heart failure; stress-induced cardiomyopathy; takotsubo cardiomyopathy (ttc); takotsubo syndrome.
Copyright © 2021, Landa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Khalid N, Ahmad SA, Shlofmitz E, Chhabra L. Pathophysiology of Takotsubo syndrome. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. - PubMed
-
- Prevalence of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy in the United States. Deshmukh A, Kumar G, Pant S, Rihal C, Murugiah K, Mehta JL. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002870312002402. Am Heart J. 2012;164:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad SA, Brito D, Khalid N, Ibrahim MA. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. - PubMed
-
- Apical ballooning syndrome (Tako-Tsubo or stress cardiomyopathy): a mimic of acute myocardial infarction. Prasad A, Lerman A, Rihal CS. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002870307009143. Am Heart J. 2008;155:408–417. - PubMed
-
- Apical and midventricular transient left ventricular dysfunction syndrome (tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy): frequency, mechanisms, and prognosis. Kurowski V, Kaiser A, von Hof K, et al. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0012369215366447. Chest. 2007;132:809–816. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources