Detecting SARS-CoV-2 From Chest X-Ray Using Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 34976572
- PMCID: PMC8675556
- DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3061621
Detecting SARS-CoV-2 From Chest X-Ray Using Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
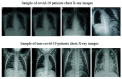
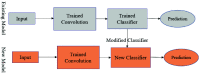
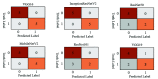
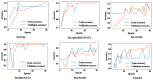
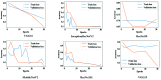
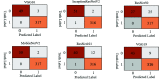
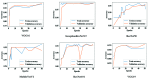
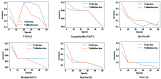
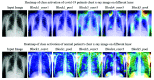
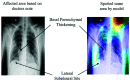
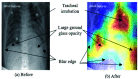
Chest radiographs (X-rays) combined with Deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) methods have been demonstrated to detect and diagnose the onset of COVID-19, the disease caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). However, questions remain regarding the accuracy of those methods as they are often challenged by limited datasets, performance legitimacy on imbalanced data, and have their results typically reported without proper confidence intervals. Considering the opportunity to address these issues, in this study, we propose and test six modified deep learning models, including VGG16, InceptionResNetV2, ResNet50, MobileNetV2, ResNet101, and VGG19 to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection from chest X-ray images. Results are evaluated in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and f- score using a small and balanced dataset (Study One), and a larger and imbalanced dataset (Study Two). With 95% confidence interval, VGG16 and MobileNetV2 show that, on both datasets, the model could identify patients with COVID-19 symptoms with an accuracy of up to 100%. We also present a pilot test of VGG16 models on a multi-class dataset, showing promising results by achieving 91% accuracy in detecting COVID-19, normal, and Pneumonia patients. Furthermore, we demonstrated that poorly performing models in Study One (ResNet50 and ResNet101) had their accuracy rise from 70% to 93% once trained with the comparatively larger dataset of Study Two. Still, models like InceptionResNetV2 and VGG19's demonstrated an accuracy of 97% on both datasets, which posits the effectiveness of our proposed methods, ultimately presenting a reasonable and accessible alternative to identify patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; chest X-ray; coronavirus; deep learning; imbalanced data; small data.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. For more information, see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Figures

References
-
- Worldometer. COVID-19 World Meter. Accessed: Aug. 6, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus
-
- Pan L., Mu M., Yang P., Sun Y., Wang R., Yan J., Li P., Hu B., Wang J., Hu C., Jin Y., Niu X., Ping R., Du Y., Li T., Xu G., Hu Q., and Tu L., “Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: A descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study,” Amer. J. Gastroenterol., vol. 115, no. 5, pp. 766–773, May 2020, doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
