Advances in Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for in Vivo Imaging in Oncology
- PMID: 34976579
- PMCID: PMC8671959
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.62970
Advances in Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for in Vivo Imaging in Oncology
Abstract
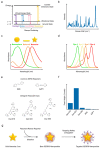
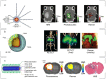
In the last two decades, the application of surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanoparticles for preclinical cancer imaging has attracted increasing attention. Raman imaging with SERS nanoparticles offers unparalleled sensitivity, providing a platform for molecular targeting, and granting multiplexed and multimodal imaging capabilities. Recent progress has been facilitated not only by the optimization of the SERS contrast agents themselves, but also by the developments in Raman imaging approaches and instrumentation. In this article, we review the principles of Raman scattering and SERS, present advances in Raman instrumentation specific to cancer imaging, and discuss the biological means of ensuring selective in vivo uptake of SERS contrast agents for targeted, multiplexed, and multimodal imaging applications. We offer our perspective on areas that must be addressed in order to facilitate the clinical translation of SERS contrast agents for in vivo imaging in oncology.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Moriyasu F, Itoh K. Efficacy of perflubutane microbubble-enhanced ultrasound in the characterization and detection of focal liver lesions: phase 3 multicenter clinical trial. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2009;193:86–95. - PubMed
-
- Smeenge M, Tranquart F, Mannaerts CK, de Reijke TM, van de Vijver MJ, Laguna MP. et al. First-in-Human Ultrasound Molecular Imaging With a VEGFR2-Specific Ultrasound Molecular Contrast Agent (BR55) in Prostate Cancer: A Safety and Feasibility Pilot Study. Invest Radiol. 2017;52:419–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

