Sirolimus-induced secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- PMID: 34976718
- PMCID: PMC8688701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101566
Sirolimus-induced secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Abstract
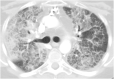
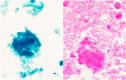
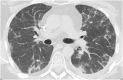
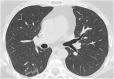
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare pulmonary syndrome that is characterized by the accumulation of excess surfactant in the alveolar space, leading to impaired gas exchange. Sirolimus-induced PAP is an extremely rare entity that has only been described in the literature in a small number of case reports. We present a case of a 39-year-old female with acute lymphocytic leukemia who underwent stem cell transplant, complicated by graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD) involving the skin for which she was treated with steroids, photopheresis, sirolimus, and ruxolitinib. She was admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) for acute on chronic hypoxic respiratory failure requiring intermittent mechanical ventilation. Computed tomography (CT) of the chest showed thickened inter- and intralobular septa with ground glass opacities and consolidation with a limited geographic pattern. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was stained with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), which was positive for extracellular proteinaceous material. Autoimmune studies including antibody levels for primary autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) were negative. The patient was diagnosed with sirolimus-induced secondary PAP, and sirolimus was discontinued. A year later, she no longer required supplemental oxygen, and repeat CT imaging showed only faint residual disease. This is the only documented case of sirolimus-induced PAP in a stem cell transplant recipient and the first case reported in which the patient developed severe hypoxic respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. In the right clinical context, PAP can be diagnosed with characteristic high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings, serum GM-CSF antibody levels, and bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Rosen S.H., Castleman B., Liebow A.A. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1958;258(23):1123–1142. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida M., Ikegami M., Reed J.A., Chroneos Z.C., Whitsett J.A. GM-CSF regulates protein and lipid catabolism by alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2001;280(3):L379–L386. - PubMed
-
- Trapnell B.C., Nakata K., Bonella F., Campo I., Griese M., Hamilton J., et al. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019;5(1):16. - PubMed
-
- deMello D.E., Lin Z. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a review. Pediatr. Pathol. Mol. Med. 2001;20(5):413–432. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein L.S., Kavuru M.S., Curtis-McCarthy P., Christie H.A., Farver C., Stoller J.K. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: clinical features and outcomes. Chest. 1998;114(5):1357–1362. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

