Collagenous gastroduodenocolitis in a Korean adolescent: first pediatric case report in Asia
- PMID: 34976776
- PMCID: PMC8649595
- DOI: 10.21037/tp-21-342
Collagenous gastroduodenocolitis in a Korean adolescent: first pediatric case report in Asia
Abstract
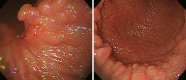
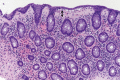
Collagenous gastritis (CG) is a rare disease diagnosed histologically by the subepithelial deposition of collagen bands thicker than 10 µm and the infiltration of inflammatory mononuclear cells in the lamina propria. The definite pathophysiology is yet to be elucidated. However, recent studies have suggested that the collagen deposition may be the result of a reparative process in response to an earlier inflammatory, autoimmune, infectious, or toxic insult. CG is divided into the pediatric- and adult-type. While the pediatric-type is limited to the stomach, the adult-type involves not only the stomach but also the intestine and/or colon. We report a rare case of adult-type CG in a 15-year-old boy who initially presented with abdominal pain and iron-deficiency anemia. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) revealed findings suspicious for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) gastritis. Although histology did not reveal the organism, campylobacter-like organism (CLO) test was positive. Based on the diagnosis of suspicious H. pylori gastritis, eradication was conducted using the triple drug regimen. However, symptoms of intermittent abdominal pain persisted and diarrhea newly developed one year later. Histologic results from biopsies from the stomach, duodenum, and colon revealed findings compatible with CG, collagenous duodenitis (CD), and collagenous colitis (CC). This is the first pediatric case of collagenous gastroduodenocolitis (CGDC) reported in Asia. It is no longer assumed that adult-type and pediatric-type CG should be classified as an independent disease, but should be considered as similar diseases on a continuous spectrum. Therefore, children and adolescents diagnosed with CG should also consider undergoing a colonoscopy for the evaluation of possible coexisting CC when concurrent lower gastrointestinal symptoms are present. Moreover, considering the possibility of negative findings on the first endoscopy, repeat endoscopy should be considered when symptoms persist.
Keywords: Case report; collagenous colitis (CC); collagenous duodenitis (CD); collagenous gastritis (CG); colonoscopy.
2021 Translational Pediatrics. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tp-21-342). YML reports that this work was supported by the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund (No. 20210021) granted to her. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
