FNDC3B and BPGM Are Involved in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Carcinogenesis of Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 34976823
- PMCID: PMC8716600
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.783868
FNDC3B and BPGM Are Involved in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Carcinogenesis of Cervical Cancer
Abstract
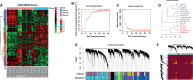
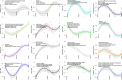
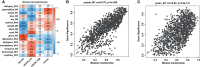
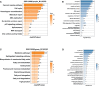
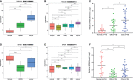
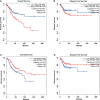
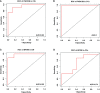
Human papillomavirus (HPV)-mediated cervical carcinogenesis is a multistep progressing from persistent infection, precancerous lesion to cervical cancer (CCa). Although molecular alterations driven by viral oncoproteins are necessary in cervical carcinogenesis, the key regulators behind the multistep process remain not well understood. It is pivotal to identify the key genes involved in the process for early diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Here we analyzed the mRNA expression profiles in cervical samples including normal, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), and CCa. A co-expression network was constructed using weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) to reveal the crucial modules in the dynamic process from HPV infection to CCa development. Furthermore, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that could distinguish all stages of progression of CCa were screened. The key genes involved in HPV-CCa were identified. It was found that the genes involved in DNA replication/repair and cell cycle were upregulated in CIN compared with normal control, and sustained in CCa, accompanied by substantial metabolic shifts. We found that upregulated fibronectin type III domain-containing 3B (FNDC3B) and downregulated bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM) could differentiate all stages of CCa progression. In patients with CCa, a higher expression of FNDC3B or lower expression of BPGM was closely correlated with a shorter overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of CIN and CCa showed that FNDC3B had the highest sensitivity and specificity for predicting CCa development. Taken together, the current data showed that FNDC3B and BPGM were key genes involved in HPV-mediated transformation from normal epithelium to precancerous lesions and CCa.
Keywords: BPGM; FNDC3B; WGCNA; cervical cancer; human papillomavirus.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Yu, Deng, Ling, Wen, Lv, Ou, Wang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FNDC3B is associated with ER stress and poor prognosis in cervical cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jan;19(1):406-414. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11098. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31897153 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Profiling of Cervical RNA-Binding Proteins Identifies Human Papillomavirus Regulation of RNASEH2A Expression by Viral E7 and E2F1.mBio. 2019 Jan 29;10(1):e02687-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02687-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30696738 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Human Papillomavirus-Associated Cervical Cancer Differentially Expressed Genes and Identification of Prognostic Factors using Integrated Bioinformatics Approaches.Adv Biomed Res. 2024 Sep 23;13:78. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_338_23. eCollection 2024. Adv Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 39512411 Free PMC article.
-
CXC chemokine receptor 7 expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.Biomed Rep. 2016 Jan;4(1):63-67. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.529. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 26870336 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Specific Gene Expression during Productive Human Papillomavirus 16 Infection of Cervical, Foreskin, and Tonsil Epithelium.J Virol. 2019 Aug 13;93(17):e00915-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00915-19. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31189705 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of fibronectin type III domain containing 3B as a potential prognostic and therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer: a preliminary analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Apr 5;29(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01823-6. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38581008 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated genomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the activation of PI3K signaling pathway in HPV-independent cervical cancers.Br J Cancer. 2024 Apr;130(6):987-1000. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02555-w. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38253702 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphosphoglycerate mutase predicts myocardial dysfunction and adverse outcome in sepsis: an observational cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Feb 7;24(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09008-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38326761 Free PMC article.
-
FNDC3B promotes gastric cancer metastasis via interacting with FAM83H and preventing its proteasomal degradation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 May 31;30(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00741-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40450207 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

