Toward the Knowledge of the Epidemiological Impact of Acute Rheumatic Fever in Italy
- PMID: 34976887
- PMCID: PMC8714836
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.746505
Toward the Knowledge of the Epidemiological Impact of Acute Rheumatic Fever in Italy
Abstract
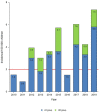
Background: To estimate the incidence of Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF) in Tuscany, a region of Central Italy, evaluating the epidemiological impact of the new diagnostic guidelines, and to analyse our outcomes in the context of the Italian overview. Methods: A multicenter and retrospective study was conducted involving children <18 years old living in Tuscany and diagnosed in the period between 2010 and 2019. Two groups were established based on the new diagnostic criteria: High-Risk (HR) group patients, n = 29 and Low-Risk group patients, n = 96. Results: ARF annual incidence ranged from 0.91 to 7.33 out of 100,000 children in the analyzed period, with peak of incidence registered in 2019. The application of HR criteria led to an increase of ARF diagnosis of 30%. Among the overall cohort joint involvement was the most represented criteria (68%), followed by carditis (58%). High prevalence of subclinical carditis was observed (59%). Conclusions: Tuscany should be considered an HR geographic area and HR criteria should be used for ARF diagnosis in this region.
Keywords: acute rheumatic fever; epidemiology; high-risk population; incidence; revised Jones criteria.
Copyright © 2021 Alberio, Pieroni, Di Gangi, Cappelli, Bini, Abu-Rumeileh, Orsini, Bonuccelli, Peroni, Assanta, Gaggiano, Simonini and Consolini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar R, Sharma YP, Thakur JS, Patro BK, Bhatia A, Singh IP, et al. Streptococcal pharyngitis, rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease: eight-year prospective surveillance in Rupnagar district of Punjab, India. Natl Med J India. (2014) 27:70–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources