Cost-Utility Analysis of Wide-Field Imaging as an Auxiliary Technology for Retinopathy of Prematurity Care in Brazil
- PMID: 34976892
- PMCID: PMC8716796
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.757258
Cost-Utility Analysis of Wide-Field Imaging as an Auxiliary Technology for Retinopathy of Prematurity Care in Brazil
Abstract
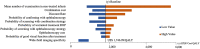
Purpose: To evaluate the cost-utility of wide-field imaging (WFI) as a complementary technology for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) screening from the Brazilian Unified Health System's perspective. Introduction: ROP is one of the leading causes of avoidable childhood blindness worldwide, especially in middle-income countries. The current ROP screening involves indirect binocular ophthalmoscopy (IBO) by ROP expert ophthalmologists. However, there is still insufficient ROP screening coverage. An alternative screening strategy is the combination of WFI with IBO. Methods: A cost-utility analysis was performed using a deterministic decision-tree simulation model to estimate incremental cost-utility for ROP care. Two screening strategies were compared: (1) IBO and (2) combination of WFI of all eligible preterm infants and IBO for type 2 ROP or worse and for non-readable images. Eligible population included preterm infants <32 weeks of gestational age or birth weight equal to or <1,500 g. The temporal horizon was lifetime. Visual outcome data was converted to utility, and the health benefits were estimated on quality-adjusted life-years (QALY). Incremental cost per QALY gained was calculated from the health system perspective. Costs were estimated considering equipment, maintenance, consumables, and staff. A micro-costing approach was used for WFI. Two technician nurses were trained for imaging execution and had their time evaluated. Two ROP expert ophthalmologists had their time evaluated for imaging reading. One-way sensitivity analysis and probabilistic sensitivity analysis were performed. Results: Combined screening strategy resulted in a cost-effective program considering 90% ROP screening coverage. Costs per examination: (1) screening with IBO: US dollar (US $) 34.36; (2) screening with combination: US $58.20; (3) laser treatment: US $642.09; (4) long-term follow-up: ranged from US $69.33 to 286.91, based on the infant's visual function. Incremental cost per QALY gained was US $1,746.99/QALY per infant screened with the combination strategy. One-way sensitivity analysis resulted in cost-effectiveness for all parameters. Probabilistic sensitivity analyses yielded a 100% probability of combination being cost-effective in a willingness-to-pay threshold of US $1,800/QALY. Conclusion: The combined strategy for ROP screening was cost-effective. It enhances access for appropriate ROP care in middle-income countries and dminishes opportunity costs for ophthalmologists.
Keywords: Brazil; costs and cost analysis; diagnosis; healthcare economics; neonatal screening; quality-adjusted life years (QALY); retinopathy of prematurity; telemedicine.
Copyright © 2021 Neves, Haefeli, Zin, Steffen, Vasconcelos and Pinto.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Eds Howson CP, Kinney MV, Lawn JE. March of Dimes, PMNCH, Save the Children, WHO. Born Too Soon: The Global Action Report on Preterm Birth. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2012).
-
- Early Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Good WV, Hardy RJ, Dobson V, Palmer EA, Phelps DL, et al. Final visual acuity results in the early treatment for retinopathy of prematurity study. Arch Ophthalmol. (2010) 128:663–71. 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.72 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

