Perspectives on Challenges to Cell Therapy Development in Taiwan: Strengthening Evidential Standards and Ways Forward
- PMID: 34976978
- PMCID: PMC8716849
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.789043
Perspectives on Challenges to Cell Therapy Development in Taiwan: Strengthening Evidential Standards and Ways Forward
Abstract
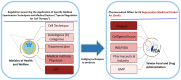
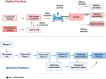
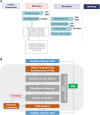
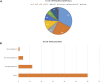
Over the past years, the field of regenerative medicine and cell therapy has garnered much interest, extending beyond the bench to broader use, and commercialization. These therapies undergo stringent regulatory oversight as a result of their complexities and potential risk across different jurisdictions. Taiwan's government, with the aim of developing the country as a hub for regenerative medicine in Asia, enacted a dual track act to promote the development of regenerative and cell therapy products. This qualitative study used purposive sampling to recruit sixteen experts (Twelve respondents from medical institutions and four respondents from the industry) to understand their perspectives on one of the regulatory tracks which governs the medical use of cell technologies and challenges regarding its implementation. Semi-structured interviews were conducted, transcribed, coded and thematically analyzed. Three major themes emerged from the analysis: 1) Perceptions of the "Special Regulation for Cell Therapy" 2) Emerging issues and controversies on the medical use of cell technologies in private clinics, and 3) Challenges impeding the clinical innovation of cell technologies. As reported by the experts, it was clear that the special regulation for cell therapy was aimed at legalizing the clinical use of cell therapy in a similar fashion to an evidence-based pathway, to promote clinical innovation, ensure manufacturing consistency, and improve oversight on cell-based therapies. Thus, the regulation addresses the issues of safety concerns, patient's access and stem cell tourism. However, the limited approved cell techniques, quality control during cell processing, time, and criteria used in evaluating applications in addition to the need to develop evidential standards for clinical evidence are some of the difficulties faced. Thus, policy interventions on funding, educational resources, training, and regulatory clarity addressing these challenges may positively impact clinical innovation of cell therapy in Taiwan.
Keywords: Taiwan; cell-based therapy; clinical evidence; qualitative research; regenerative medicine; regulation.
Copyright © 2021 Abolarinwa, Shaw and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Commission Directive (EU) (2015). Commission Directive (EU) 2015/566 of 8 April 2015 implementing Directive 2004/23/EC as regards the procedures for verifying the equivalent standards of quality and safety of imported tissues and cells Text with EEA relevance. OJ L 93, 56–68.
-
- Braun V., Clarke V. (2006). Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3, 77–101. 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

