Using Unnatural Protein Fusions to Engineer a Coenzyme Self-Sufficiency System for D-Phenyllactic Acid Biosynthesis in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 34976983
- PMCID: PMC8718758
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.795885
Using Unnatural Protein Fusions to Engineer a Coenzyme Self-Sufficiency System for D-Phenyllactic Acid Biosynthesis in Escherichia coli
Abstract
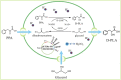
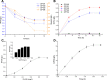
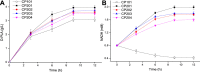
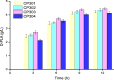
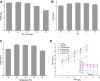
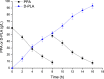
The biosynthetic production of D-penyllactic acid (D-PLA) is often affected by insufficient supply and regeneration of cofactors, leading to high production cost, and difficulty in industrialization. In this study, a D-lactate dehydrogenase (D-LDH) and glycerol dehydrogenase (GlyDH) co-expression system was constructed to achieve coenzyme NADH self-sufficiency and sustainable production of D-PLA. Using glycerol and sodium phenylpyruvate (PPA) as co-substrate, the E. coli BL21 (DE3) harboring a plasmid to co-express LfD-LDH and BmGlyDH produced 3.95 g/L D-PLA with a yield of 0.78 g/g PPA, similar to previous studies. Then, flexible linkers were used to construct fusion proteins composing of D-LDH and GlyDH. Under the optimal conditions, 5.87 g/L D-PLA was produced by expressing LfD-LDH-l3-BmGlyDH with a yield of 0.97 g/g PPA, which was 59.3% increased compared to expression of LfD-LDH. In a scaled-up reaction, a productivity of 5.83 g/L/h was reached. In this study, improving the bio-catalytic efficiency by artificial redox self-equilibrium system with a bifunctional fusion protein could reduce the bio-production cost of D-PLA, making this bio-production of D-PLA a more promising industrial technology.
Keywords: D-PLA; coenzyme self-sufficiency; d-Lactate dehydrogenase; fusion protein; glycerol dehydrogenase; phenyllactic acid.
Copyright © 2021 Qin, Wang, Luo, Li, Xiong and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abadli M., Dewasme L., Tebbani S., Dumur D., Vande Wouwer A. (2021). An Experimental Assessment of Robust Control and Estimation of Acetate Concentration in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) Fed-Batch Cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 174, 108103. 10.1016/j.bej.2021.108103 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

