Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 34977024
- PMCID: PMC8714905
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.774370
Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
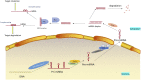
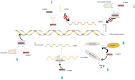
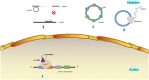
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease that is pervasive in life, and the incidence and mortality of OA are increasing, causing many adverse effects on people's life. Therefore, it is very vital to identify new biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of OA. ncRNA is a nonprotein-coding RNA that does not translate into proteins but participates in protein translation. At the RNA level, it can perform biological functions. Many studies have found that miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA are closely related to the course of OA and play important regulatory roles in transcription, post-transcription, and post-translation, which can be used as biological targets for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of OA. In this review, we summarized and described the various roles of different types of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in OA, the roles of different lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in OA, and the possible prospects of these ncRNAs in clinical application.
Keywords: circRNA; lncRNA; lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis; miRNA; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Kong, Sun, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Therapeutic Potential and Role of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in Osteoarthritis.Curr Gene Ther. 2019;19(4):255-263. doi: 10.2174/1566523219666190716092203. Curr Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 31333128 Review.
-
Research progress on the circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in gastric cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Oct;238:154030. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154030. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36116329 Review.
-
Interactions Among lncRNA/circRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Musculoskeletal Degenerative Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 11;9:753931. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.753931. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34708047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA expression profile of articular chondrocytes in an IL-1β-induced mouse model of osteoarthritis.Gene. 2018 Feb 20;644:20-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.12.020. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29247798
-
Comprehensive analysis of the whole coding and non-coding RNA transcriptome expression profiles and construction of the circRNA-lncRNA co-regulated ceRNA network in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Funct Integr Genomics. 2019 Jan;19(1):109-121. doi: 10.1007/s10142-018-0631-y. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Funct Integr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30128795
Cited by
-
Circ-NFKB1 sponges miR-203a-5p to regulate ERBB4 expression and promotes IL-1β induced chondrocytes apoptosis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jul 25;18(1):528. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03990-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37491357 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA RMRP promotes chondrocyte injury by regulating the FOXC1/RBP4 axis.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024;49(4):366-382. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2024.145312. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39944260 Free PMC article.
-
High Mobility Group Proteins in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 2;13:911152. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.911152. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Compounds and Their Chondroprotective Effects for Osteoarthritis Amelioration: A Focus on Nanotherapeutic Strategies, Epigenetic Modifications, and Gut Microbiota.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 22;16(21):3587. doi: 10.3390/nu16213587. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA-mediated cartilage homeostasis in osteoarthritis: a narrative review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 21;11:1326843. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1326843. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38449881 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

