The Tongue Squamous Carcinoma Cell Line Cal27 Primarily Employs Integrin α6β4-Containing Type II Hemidesmosomes for Adhesion Which Contribute to Anticancer Drug Sensitivity
- PMID: 34977030
- PMCID: PMC8716755
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.786758
The Tongue Squamous Carcinoma Cell Line Cal27 Primarily Employs Integrin α6β4-Containing Type II Hemidesmosomes for Adhesion Which Contribute to Anticancer Drug Sensitivity
Abstract
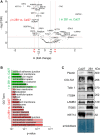
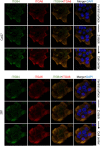
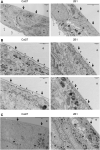
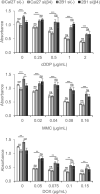
Integrins are heterodimeric cell surface glycoproteins used by cells to bind to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and regulate tumor cell proliferation, migration and survival. A causative relationship between integrin expression and resistance to anticancer drugs has been demonstrated in different tumors, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Using a Cal27 tongue squamous cell carcinoma model, we have previously demonstrated that de novo expression of integrin αVβ3 confers resistance to several anticancer drugs (cisplatin, mitomycin C and doxorubicin) through a mechanism involving downregulation of active Src, increased cell migration and invasion. In the integrin αVβ3 expressing Cal27-derived cell clone 2B1, αVβ5 expression was also increased, but unrelated to drug resistance. To identify the integrin adhesion complex (IAC) components that contribute to the changes in Cal27 and 2B1 cell adhesion and anticancer drug resistance, we isolated IACs from both cell lines. Mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics analysis indicated that both cell lines preferentially, but not exclusively, use integrin α6β4, which is classically found in hemidesmosomes. The anticancer drug resistant cell clone 2B1 demonstrated an increased level of α6β4 accompanied with increased deposition of a laminin-332-containing ECM. Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy demonstrated the formation of type II hemidesmosomes by both cell types. Furthermore, suppression of α6β4 expression in both lines conferred resistance to anticancer drugs through a mechanism independent of αVβ3, which implies that the cell clone 2B1 would have been even more resistant had the upregulation of α6β4 not occurred. Taken together, our results identify a key role for α6β4-containing type II hemidesmosomes in regulating anticancer drug sensitivity.
Keywords: adhesome; anticancer drug sensitivity; hemidesmosome; integrin alpha 6 beta 4; integrin alpha v beta 3; integrin crosstalk; keratins 5/14; laminin-332.
Copyright © 2021 Tadijan, Humphries, Samaržija, Stojanović, Zha, Čuljak, Tomić, Paradžik, Nestić, Kang, Humphries and Ambriović-Ristov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ambriović-Ristov A., Gabrilovac J., Čimbora-Zovko T., Osmak M. (2004). Increased Adenoviral Transduction Efficacy in Human Laryngeal Carcinoma Cells Resistant to Cisplatin Is Associated with Increased Expression of Integrin ?v?3 and coxsackie Adenovirus Receptor. Int. J. Cancer 110 (5), 660–667. 10.1002/ijc.20176 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atanasova V. S., Russell R. J., Webster T. G., Cao Q., Agarwal P., Lim Y. Z., et al. (2019). Thrombospondin-1 Is a Major Activator of TGF-β Signaling in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Fibroblasts. J. Invest. Dermatol. 139 (7), 1497–1505. Elsevier B.V.e5. 10.1016/j.jid.2019.01.011 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

