Ferroptosis Signaling and Regulators in Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 34977044
- PMCID: PMC8716792
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.809457
Ferroptosis Signaling and Regulators in Atherosclerosis
Abstract
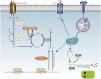
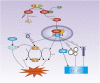
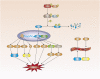
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a major cause of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease, heart failure and stroke. Abnormal lipid metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation are the main features of AS. Ferroptosis is an iron-driven programmed cell death characterized by lipid peroxidation, which have been proved to participate in the development and progression of AS by different signal pathways. NRF2-Keap1 pathway decreases ferroptosis associated with AS by maintaining cellular iron homeostasis, increasing the production glutathione, GPX4 and NADPH. The p53 plays different roles in ferroptosis at different stages of AS in a transcription-dependent and transcription- independent manner. The Hippo pathway is involved in progression of AS, which has been proved the activation of ferroptosis. Other transcription factors, such as ATF3, ATF4, STAT3, also involved in the occurrence of ferroptosis and AS. Certain proteins or enzymes also have a regulatory role in AS and ferroptosis. In this paper, we review the mechanism of ferroptosis and its important role in AS in an attempt to find a new relationship between ferroptosis and AS and provide new ideas for the future treatment of AS.
Keywords: Hippo; Nrf2; atherosclerosis; ferroptosis; p53.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Zhao, Ye, Yang, Shen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

