Impact of Plasma 5 Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid, a Serotonin Metabolite, on Clinical Severity in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 34977089
- PMCID: PMC8716548
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.785409
Impact of Plasma 5 Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid, a Serotonin Metabolite, on Clinical Severity in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
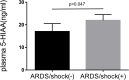
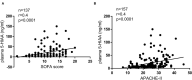
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by dysregulated vascular permeability. The clinical outcomes remain poor, and the disease burden is widespread. We demonstrated that plasma 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), a serotonin metabolite, is a pivotal severity indicator of ARDS. Serotonin is an effector of cellular contraction and a modulator of vascular permeability. Plasma 5-HIAA levels were significantly elevated in severe ARDS cases with shock status (p = 0.047) and positively correlated with SOFA (p < 0.0001) and APACHE-II score (p < 0.0001). In the longitudinal analysis, plasma 5-HIAA levels were also a strong independent predictor of mortality rate (p = 0.005). This study indicates that plasma 5-HIAA is a biomarker of ARDS severity and highlights the importance of evaluating vascular leakage levels for ARDS treatment.
Keywords: 5-HIAA (5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid); ARDS; serotonin; shock; vascular permeability.
Copyright © 2021 Tanaka, Mori, Tashiro and Izumikawa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

