Sonographic Tophi and Inflammation Are Associated With Carotid Atheroma Plaques in Gout
- PMID: 34977097
- PMCID: PMC8716736
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.795984
Sonographic Tophi and Inflammation Are Associated With Carotid Atheroma Plaques in Gout
Abstract
Objective: Gout and cardiovascular disease are closely related, but the mechanism connecting them remains unknown. This study aims to explore whether urate crystal deposits and inflammation (assessed by ultrasound) are associated with carotid atherosclerosis. Methods: We included consecutive patients with crystal-proven gout newly presenting to a tertiary rheumatology unit. Patients under urate-lowering treatment were excluded. Ultrasound assessment was performed during intercritical periods. Musculoskeletal scans evaluated six joints and four tendons for urate crystal deposits (double contour, aggregates, and tophi), and power Doppler (PD) signal (graded 0-3) as a marker of local inflammation. The sum of locations showing deposits or a positive PD signal (≥1) was registered. Carotids were scanned for increased intima-media thickness (IMT) and atheroma plaques, according to the Mannheim consensus. Associations were analyzed using logistic regression. Results: The study included 103 patients showing sonographic crystal deposits at the examined locations (mean sum 9.9, minimum 2); tophi were the most frequent. Two-thirds of participants presented a positive PD signal (30.1% grade 2-3). In the carotid scans, 59.2% of participants showed atheroma plaques, and 33.0% increased IMT. Tophi (odds ratio [OR] 1.24; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.03-1.50) and a positive PD signal (OR 1.67; 95% CI 1.09-2.56) were significantly associated with atheroma plaques, while an increased IMT showed no sonographic association. Conclusion: Sonographic crystal deposits and subclinical inflammation were consistently observed in patients with intercritical gout. Tophi and a positive PD signal were linked to carotid atherosclerosis. Our findings may contribute to understanding the complex relationship between gout and atherosclerosis.
Keywords: carotid artery diseases; gout; inflammation; power Doppler; tophi; ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2021 Calabuig, Martínez-Sanchis and Andrés.
Conflict of interest statement
MA declares consultancies and speaking fees from Menarini and Grünenthal. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
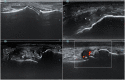
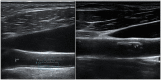
References
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1736–88. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Disveld IJM, Zoakman S, Jansen TLTA, Rongen GA, Kienhorst LBE, Janssens HJEM, et al. Crystal-proven gout patients have an increased mortality due to cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases especially when having tophi and/or high serum uric acid levels: a prospective cohort study. Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 38:1385–91. 10.1007/s10067-019-04520-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

