Two compound techniques for total body irradiation
- PMID: 34977366
- PMCID: PMC8683645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2021.11.006
Two compound techniques for total body irradiation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Two compound techniques for total body irradiation" [Tech. Innov. Patient Support Radiat. Oncol. 21 (2022) 1-7].Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2023 Jan 11;25:100199. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2022.12.006. eCollection 2023 Mar. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36659910 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Total body irradiation (TBI) is an important treatment modality that is used in combination with chemotherapy in many stem cell transplantation protocols. Therefore, the quality of the irradiation is important. Two techniques for planning and delivering TBI are presented and compared.
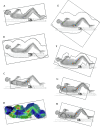
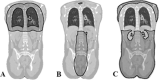
Methods and materials: The technique named ExIMRT is a combination of manually shaped conventional fields from an extended SSD and isocentric IMRT fields. The technique named ExVMAT is a combination of conventional and IMRT fields from an extended SSD and isocentric VMAT fields. Dosimetric data from 32 patients who were planned and treated according to one of the two techniques were compared.
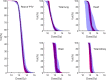
Results: When comparing the two techniques, it is determined that the ExVMAT technique is able to significantly reduce the mean total volume overdosed by 120% from 408 to 12 cm3. The dose covering 98% of the total lung volume is significantly increased by this technique from a mean of 9.7 Gy to 10.3 Gy. Additionally, the dose covering 2% of the total kidney volume is significantly decreased from a mean of 12.8 to 12.5 Gy. Furthermore, the population-based variance of the median dose to the total lung volume, the heart and the volume of the body prescribed to 12.5 Gy is significantly reduced. The results are obtained without compromising overall treatment quality as treatment time or dose rate to the lungs.
Conclusion: Using the ExVMAT technique, a superior dose distribution can be delivered both from a patient and a population perspective compared to the ExIMRT technique.
Keywords: IMRT; RILI; Total body irradiation; Treatment planning; VMAT.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Wills C., Cherian S., Yousef J., Wang K., Mackley H.B. Total body irradiation: A practical review. Appl Rad Oncol. 2016;5:11–17. https://appliedradiationoncology.com/articles/total-body-irradiation-a-p...
-
- Potdar R.R., Gupta S., Giebel S., Savani B.N., Varadi G., Nagler A., et al. Current status and perspectives of irradiation-based conditioning regimens for patients with acute leukemia undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Hematol Int. 2019;1(1):19. doi: 10.2991/chi.d.190218.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

