Oral etoposide and zosuquidar bioavailability in rats: Effect of co-administration and in vitro- in vivo correlation of P-glycoprotein inhibition
- PMID: 34977557
- PMCID: PMC8683663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2021.100089
Oral etoposide and zosuquidar bioavailability in rats: Effect of co-administration and in vitro- in vivo correlation of P-glycoprotein inhibition
Abstract
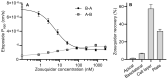
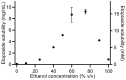
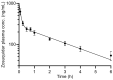
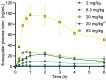
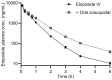
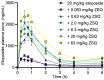
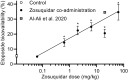
P-glycoprotein inhibitors, like zosuquidar, have widely been used to study the role of P-glycoprotein in oral absorption. Still, systematic studies on the inhibitor dose-response relationship on intestinal drug permeation are lacking. In the present study, we investigated the effect of 0.79 nM-2.5 μM zosuquidar on etoposide permeability across Caco-2 cell monolayers. We also investigated etoposide pharmacokinetics after oral or IV administration to Sprague Dawley rats with co-administration of 0.063-63 mg/kg zosuquidar, as well as the pharmacokinetics of zosuquidar itself. Oral zosuquidar bioavailability was 2.6-4.2%, while oral etoposide bioavailability was 5.5 ± 0.9%, which increased with increasing zosuquidar doses to 35 ± 5%. The intestinal zosuquidar concentration required to induce a half-maximal increase in bioavailability was estimated to 180 μM. In contrast, the IC50 of zosuquidar on etoposide permeability in vitro was only 5-10 nM, and a substantial in vitro-in vivo discrepancy of at least four orders of magnitude was thereby identified. Overall, the present study provides valuable insights for future formulation development that applies fixed dose combinations of P-glycoprotein inhibitors to increase the absorption of poorly permeable P-glycoprotein substrate drugs.
Keywords: Caco-2; Efflux transport; Etoposide; Oral absorption; P-glycoprotein; Zosuquidar; in vitro-in vivo correlation.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial og personal interests.
Figures

References
-
- Adane E.D., Liu Z., Xiang T.-X., Anderson B.D., Leggas M. Pharmacokinetic modeling to assess factors affecting the oral bioavailability of the lactone and carboxylate forms of the lipophilic camptothecin analogue AR-67 in rats. Pharm. Res. 2012;29:1722–1736. doi: 10.1007/s11095-011-0617-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Ali A.A.A., Steffansen B., Holm R., Nielsen C.U. Nonionic surfactants increase digoxin absorption in Caco-2 and MDCKII MDR1 cells: impact on P-glycoprotein inhibition, barrier function, and repeated cellular exposure. Int. J. Pharm. 2018;551:270–280. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.09.039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Ali A.A.A., Sandra L., Versweyveld D., Pijpers I., Dillen L., Vermeulen A., Snoeys J., Holm R., Nielsen C.U. High-dose etoposide formulations do not saturate intestinal P-glycoprotein: development, stability, and pharmacokinetics in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2020;583:119399. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119399. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

