Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Apremilast in Belgian Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from the Prospective Observational APOLO Study
- PMID: 34977986
- PMCID: PMC8866349
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-02016-x
Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Apremilast in Belgian Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from the Prospective Observational APOLO Study
Abstract
Introduction: Apremilast is approved for the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Real-world evidence on the efficacy and safety of apremilast in clinical practice is limited. We assessed the use of apremilast in patients with PsA in Belgium clinical practice.
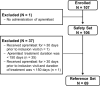
Methods: The multicentre, observational, prospective APOLO study enrolled patients with active PsA initiating apremilast in Belgium between April 2017 and December 2018. Primary outcome was PsA Response Criteria (PsARC) after 6 months of apremilast treatment. Secondary outcomes included PsA Impact of Disease 12 (PsAID12) and Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Disease-specific outcomes and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were analysed for patients who received apremilast within 30 days prior to their study inclusion and completed at least 150 days of treatment (reference set [REF]).
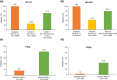
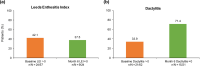
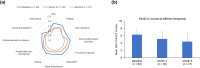
Results: Of 107 patients enrolled in the study, 106 received at least one dose of apremilast and 69 were included in the REF. PsARC response was achieved by 43.5% of patients (30/69) in the REF at month 6; mean global and composite scores including 68-joint count for pain/tenderness (68-TJC) and 66-joint count for swelling (66-SJC) improved, and 27% and 42% of patients with 68-TJC and 66-SJC > 0 at baseline had complete joint count resolution, respectively. Mean global and composite PsAID12 and HAQ-DI scores decreased at 6 months, indicating improved quality of life. Apremilast was well tolerated and the reported adverse events were in line with the known safety profile.
Conclusion: Results from the APOLO study indicate that treatment with apremilast in Belgian clinical practice improves the signs and symptoms of PsA as well as patient quality of life. CLINICALTRIALS.
Gov identifier: NCT03096990.
Keywords: Apremilast; Patient-reported outcome; Psoriatic arthritis; Real-world evidence.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. 2006:1–10. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-cl.... Accessed Aug 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

