First Identified Case of Fatal Fulminant Necrotizing Eosinophilic Myocarditis Following the Initial Dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine (BNT162b2, Comirnaty): an Extremely Rare Idiosyncratic Hypersensitivity Reaction
- PMID: 34978002
- PMCID: PMC8720536
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-021-01187-0
First Identified Case of Fatal Fulminant Necrotizing Eosinophilic Myocarditis Following the Initial Dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine (BNT162b2, Comirnaty): an Extremely Rare Idiosyncratic Hypersensitivity Reaction
Abstract
Rationale: Transient myopericarditis has been recognised as an uncommon and usually mild adverse event predominantly linked to mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. These have mostly occurred in young males after the second dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
Objectives: Fulminant necrotising eosinophilic myocarditis triggered by a variety of drugs or vaccines is an extremely rare hypersensitivity reaction carrying a substantial mortality risk. Early recognition of this medical emergency may facilitate urgent hospital admission for investigation and treatment. Timely intervention can lead to complete cardiac recovery, but the non-specific clinical features and rarity make early diagnosis challenging.
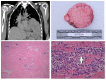
Findings: The clinical and pathological observations from a case of fatal fulminant necrotising myocarditis in a 57-year-old woman, following the first dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, are described. Other causes have been discounted with reasonable certainty.
Conclusion: These extremely rare vaccine-related adverse events are much less common than the risk of myocarditis and other lethal complications from COVID-19 infection. The benefits of vaccination far exceed the risks of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; adverse events; autopsy; death; eosinophil; hypersensitivity; myocarditis; vaccine.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
First Identified Case of Fatal Fulminant Eosinophilic Myocarditis Following the Initial Dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine (BNT162b2, Comirnaty): an Extremely Rare Idiosyncratic Necrotizing Hypersensitivity Reaction Different to Hypersensitivity or Drug-Induced Myocarditis.J Clin Immunol. 2022 May;42(4):736-737. doi: 10.1007/s10875-022-01228-2. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35178640 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

