A robust, accurate, sensitive LC-MS/MS method to measure indoxyl sulfate, validated for plasma and kidney cells
- PMID: 34978088
- PMCID: PMC9285569
- DOI: 10.1002/bmc.5307
A robust, accurate, sensitive LC-MS/MS method to measure indoxyl sulfate, validated for plasma and kidney cells
Abstract
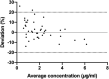
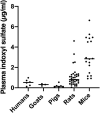
Proximal tubular damage is an important prognostic determinant in various chronic kidney diseases (CKDs). Currently available diagnostic methods do not allow for early disease detection and are neither efficient. Indoxyl sulfate (IS) is an endogenous metabolite and protein-bound uremic toxin that is eliminated via renal secretion, but accumulates in plasma during tubular dysfunction. Therefore, it may be suitable as a tubular function marker. To evaluate this, a fast bioanalytical method was developed and validated for IS in various species and a kidney cell line using LC-MS/MS. An isotope-labeled IS potassium salt as an internal standard and acetonitrile (ACN) as a protein precipitant were used for sample pretreatment. The analyte was separated on a Polaris 3 C18-A column by gradient elution using 0.1% formic acid in water and ACN, and detected by negative electrospray ionization in selected reaction monitoring mode. The within-day (≤ 4.0%) and between-day (≤ 4.3%) precisions and accuracies (97.7 to 107.3%) were within the acceptable range. The analyte showed sufficient stability at all conditions investigated. Finally, applying this assay, significantly higher plasma and lower urine concentrations of IS were observed in mice with diabetic nephropathy with tubular damage, which encourages validation toward its use as a biomarker.
Keywords: LC-MS/MS; chronic kidney diseases; indoxyl sulfate; renal tubular function; uremic toxins.
© 2022 The Authors. Biomedical Chromatography published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for measurement of a gut-derived uremic toxin panel in human serum: An application in patients with kidney disease.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Sep 10;174:618-624. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.06.033. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 31276982 Free PMC article.
-
Two rapid, accurate liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry methods for the quantification of seven uremic toxins: An application for describing their accumulation kinetic profile in a context of acute kidney injury.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;1152:122234. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122234. Epub 2020 Jun 13. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32615535
-
Simultaneous quantitative analysis of uremic toxins by LC-MS/MS with a reversed-phase/cation-exchange/anion-exchange tri-modal mixed-mode column.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Nov 15;1068-1069:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 5. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 29024911
-
Assessment of uremic toxins in advanced chronic kidney disease patients on maintenance hemodialysis by LC-ESI-MS/MS.Metabolomics. 2023 Feb 24;19(3):14. doi: 10.1007/s11306-023-01978-z. Metabolomics. 2023. PMID: 36826619
-
Reliable and Easy-To-Use Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Quantification of Olorofim (F901318), a Novel Antifungal Drug, in Human Plasma and Serum.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Oct 24;62(11):e01356-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01356-18. Print 2018 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30150474 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Determination of indoxyl sulfate by spectrofluorimetric method in human plasma through extraction with deep eutectic solvent.BMC Chem. 2024 Mar 30;18(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01172-9. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38555438 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analytical Methods for the Quantitation of p-Cresol Sulfate and Indoxyl Sulfate in Human Matrices: Biological Applications and Diagnostic Potentials.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 30;16(6):743. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060743. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine improved diabetic kidney disease through targeting gut microbiota.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):423-435. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2351946. Epub 2024 May 17. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38757785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging and spatially resolved mass spectrometry applications in nephrology.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 Jun;21(6):399-416. doi: 10.1038/s41581-025-00946-1. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40148534 Review.
-
Analysis of indoxyl sulfate in biological fluids with emphasis on sample preparation techniques: A comprehensive analytical review.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 23;10(15):e35032. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35032. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barreto, F. C. , Barreto, D. V. , Liabeuf, S. , Meert, N. , Glorieux, G. , Temmar, M. , Choukroun, G. , Vanholder, R. , & Massy, Z. A. (2009). Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with vascular disease and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 4, 1551–1558. 10.2215/CJN.03980609 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research , & Center for Veterinary Medicine . (2020). Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry. Accessed August 19, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents...
-
- Chiu, M. L. , Lawi, W. , Snyder, S. T. , Wong, P. K. , Liao, J. C. , & Gau, V. (2010). Matrix effects—A challenge toward automation of molecular analysis. JALA: Journal of the Association for Laboratory Automation, 15, 233–242. 10.1016/j.jala.2010.02.001 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

