Evaluation of Urea-Based Inhibitors of the Dopamine Transporter Using the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 34978174
- PMCID: PMC9365315
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00647
Evaluation of Urea-Based Inhibitors of the Dopamine Transporter Using the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Evaluation of Urea-Based Inhibitors of the Dopamine Transporter Using the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis".ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022 Nov 2;13(21):3138. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00459. Epub 2022 Oct 20. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36264675 No abstract available.
Abstract
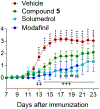
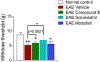
The dopaminergic system is involved in the regulation of immune responses in various homeostatic and disease conditions. For conditions such as Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis (MS), pharmacological modulation of dopamine (DA) system activity is thought to have therapeutic relevance, providing the basis for using dopaminergic agents as a treatment of relevant states. In particular, it was proposed that restoration of DA levels may inhibit neuroinflammation. We have recently reported a new class of dopamine transporter (DAT) inhibitors with high selectivity to the DAT over other G-protein coupled receptors tested. Here, we continue their evaluation as monoamine transporter inhibitors. Furthermore, we show that the urea-like DAT inhibitor (compound 5) has statistically significant anti-inflammatory effects and attenuates motor deficits and pain behaviors in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model mimicking clinical signs of MS. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the beneficial effects of DAT inhibitor-based treatment in animals with induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and the observed results provide additional support to the model of DA-related neuroinflammation.
Keywords: dopamine; dopamine transporter inhibitor; modafinil; multiple sclerosis; neuroinflammation.
Figures

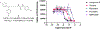
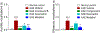


References
-
- Contreras F; Prado C; Gonzalez H; Franz D; Osorio-Barrios F; Osorio F; Ugalde V; Lopez E; Elgueta D; Figueroa A; Lladser A; Pacheco R Dopamine Receptor D3 Signaling on CD4+ T Cells Favors Th1- and Th17-Mediated Immunity. J. Immunol 2016, 196, 4143–4149. - PubMed
-
- Cosentino M; Fietta AM; Ferrari M; Rasini E; Bombelli R; Carcano E; Saporiti F; Meloni F; Marino F; Lecchini S Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells selectively express tyrosine hydroxylase and contain endogenous catecholamines subserving an autocrine/paracrine inhibitory functional loop. Blood 2007, 109, 632–642. - PubMed
-
- Mignini F; Sabbatini M; Capacchietti M; Amantini C; Bianchi E; Artico M; Tammaro A T-cell subpopulations express a different pattern of dopaminergic markers in intra- and extra-thymic compartments. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2013, 27, 463–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

