The effectiveness of mRNA-1273 vaccine against COVID-19 caused by Delta variant: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34978339
- PMCID: PMC9015635
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27568
The effectiveness of mRNA-1273 vaccine against COVID-19 caused by Delta variant: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
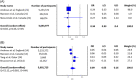
We aimed to perform meta-analyses to summarize the overall effectiveness of the mRNA-1273 vaccine against COVID-19 caused by the Delta variant from real-world studies. A systematic literature search with no language restriction was performed in electronic databases to identify eligible observational studies that reported the effectiveness of the mRNA-1273 vaccine to prevent reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) confirmed COVID-19 caused by Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.617.2). A random-effects meta-analysis model was used to estimate the pooled odds ratio (OR) at a 95% confidence interval (CI), and the vaccine effectiveness was indicated as (pooled OR - 1)/OR. Five studies were included for this systematic review and meta-analysis. The meta-analysis revealed that the administration of mRNA-1273 vaccine protected against RT-PCR confirmed COVID-19 caused by Delta variant ≥21 days post first dose, with pooled vaccine effectiveness of 66% (95% CI: 65%-67%), as well as ≥14 days after the second dose, with pooled vaccine effectiveness of 91% (95% CI: 84%-95%). In conclusion, the mRNA-1273 vaccine offers a substantial protection rate against RT-PCR confirmed COVID-19 caused by the Delta variant upon full vaccination, although with slightly reduced effectiveness relative to other strains of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: coronavirus; disease control; pathogenesis; respiratory tract; vaccines/vaccine strains; virus classification.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Weinberg GA, Szilagyi PG. Vaccine epidemiology: efficacy, effectiveness, and the translational research roadmap. J Infect Dis. 2010;201(11):1607‐1610. - PubMed
-
- Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D, et al. The Newcastle‐Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta‐analyses. Accessed September 28, 2021. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
-
- Andrews N, Tessier E, Stowe J, et al. Vaccine effectiveness and duration of protection of Comirnaty, Vaxzevria and Spikevax against mild and severe COVID‐19 in the UK. medRxiv. 2021.
-
- Nasreen S, He S, Chung H, et al. Effectiveness of COVID‐19 vaccines against variants of concern in Ontario, Canada. medRxiv. 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous