Assessing reproducibility of inherited variants detected with short-read whole genome sequencing
- PMID: 34980216
- PMCID: PMC8722114
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02569-8
Assessing reproducibility of inherited variants detected with short-read whole genome sequencing
Abstract
Background: Reproducible detection of inherited variants with whole genome sequencing (WGS) is vital for the implementation of precision medicine and is a complicated process in which each step affects variant call quality. Systematically assessing reproducibility of inherited variants with WGS and impact of each step in the process is needed for understanding and improving quality of inherited variants from WGS.
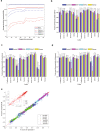
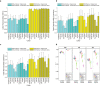
Results: To dissect the impact of factors involved in detection of inherited variants with WGS, we sequence triplicates of eight DNA samples representing two populations on three short-read sequencing platforms using three library kits in six labs and call variants with 56 combinations of aligners and callers. We find that bioinformatics pipelines (callers and aligners) have a larger impact on variant reproducibility than WGS platform or library preparation. Single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), particularly outside difficult-to-map regions, are more reproducible than small insertions and deletions (indels), which are least reproducible when > 5 bp. Increasing sequencing coverage improves indel reproducibility but has limited impact on SNVs above 30×.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight sources of variability in variant detection and the need for improvement of bioinformatics pipelines in the era of precision medicine with WGS.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Cheng DT, Prasad M, Chekaluk Y, Benayed R, Sadowska J, Zehir A, Syed A, Wang YE, Somar J, Li Y, Yelskaya Z, Wong D, Robson ME, Offit K, Berger MF, Nafa K, Ladanyi M, Zhang L. Comprehensive detection of germline variants by MSK-IMPACT, a clinical diagnostic platform for solid tumor molecular oncology and concurrent cancer predisposition testing. BMC Med Genomics. 2017;10(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12920-017-0271-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Din S, Wong K, Mueller MF, Oniscu A, Hewinson J, Black CJ, Miller ML, Jimenez-Sanchez A, Rabbie R, Rashid M, et al. Mutational analysis identifies therapeutic biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(20):5133–5142. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3713. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haapaniemi EM, Kaustio M, Rajala HL, van Adrichem AJ, Kainulainen L, Glumoff V, Doffinger R, Kuusanmaki H, Heiskanen-Kosma T, Trotta L, et al. Autoimmunity, hypogammaglobulinemia, lymphoproliferation, and mycobacterial disease in patients with activating mutations in STAT3. Blood. 2015;125(4):639–648. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-570101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wright GEB, Collins JA, Kay C, McDonald C, Dolzhenko E, Xia Q, Becanovic K, Drogemoller BI, Semaka A, Nguyen CM, et al. Length of uninterrupted CAG, independent of polyglutamine size, results in increased somatic instability, hastening onset of Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2019;104(6):1116–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.04.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

