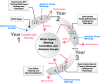
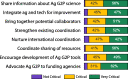
The Agricultural Genome to Phenome Initiative (AG2PI): creating a shared vision across crop and livestock research communities
- PMID: 34980221
- PMCID: PMC8722016
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02570-1
The Agricultural Genome to Phenome Initiative (AG2PI): creating a shared vision across crop and livestock research communities
Conflict of interest statement
Tuggle, Clarke, Dekkers, Ertl, Lawrence-Dill, Lyons, Murdoch, and Schnable are on the executive board of the Agricultural Genome To Phenome Initiative. Tuggle is co-lead of the Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes consortium and is a recipient of research funding from Recombinetics, Inc. Ertl is an executive committee member of the Genomes to Fields Initiative. Lyons is the principal investigator of CyVerse funded by the NSF and a Founder of uPetsia, Inc. Scott is the project manager for the USDA-NIFA funded Agricultural Genome to Phenome Initiative. Schnable is a co-lead of the Genomes to Fields Initiative; co-founder of Data2Bio, LLC; Dryland Genetics, Inc; EnGeniousAg, LLC; and LookAhead Breeding, LLC; a member of the scientific advisory board and a shareholder of Hi-Fidelity Genetics, Inc.; a member of the scientific advisory boards of Kemin Industries and Centro de Tecnologia Canavieira; and a recipient of research funding from Iowa Corn and Bayer Crop Science.
Figures
References
-
- National Research Council. A new biology for the 21st century. Washington (DC); 2009. 10.17226/12764.
-
- Lawrence-Dill CJ, Schnable PS, Springer NM. Idea factory: the maize genomes to fields initiative. Crop Sci. 2019;59(4):1406–1410. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2019.02.0071. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources