Assessing Global Kidney Nutrition Care
- PMID: 34980675
- PMCID: PMC8763143
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07800621
Assessing Global Kidney Nutrition Care
Abstract
Background and objectives: Nutrition intervention is an essential component of kidney disease management. This study aimed to understand current global availability and capacity of kidney nutrition care services, interdisciplinary communication, and availability of oral nutrition supplements.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: The International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM), working in partnership with the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) Global Kidney Health Atlas Committee, developed this Global Kidney Nutrition Care Atlas. An electronic survey was administered among key kidney care stakeholders through 182 ISN-affiliated countries between July and September 2018.
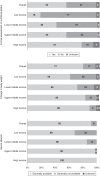
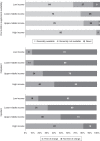
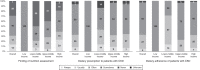
Results: Overall, 160 of 182 countries (88%) responded, of which 155 countries (97%) answered the survey items related to kidney nutrition care. Only 48% of the 155 countries have dietitians/renal dietitians to provide this specialized service. Dietary counseling, provided by a person trained in nutrition, was generally not available in 65% of low-/lower middle-income countries and "never" available in 23% of low-income countries. Forty-one percent of the countries did not provide formal assessment of nutrition status for kidney nutrition care. The availability of oral nutrition supplements varied globally and, mostly, were not freely available in low-/lower middle-income countries for both inpatient and outpatient settings. Dietitians and nephrologists only communicated "sometimes" on kidney nutrition care in ≥60% of countries globally.
Conclusions: This survey reveals significant gaps in global kidney nutrition care service capacity, availability, cost coverage, and deficiencies in interdisciplinary communication on kidney nutrition care delivery, especially in lower-income countries.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; dietitians; global; global health; kidney nutrition care; nutrition supplement; nutritional status; renal nutrition.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Accessibility of Nutrition Care for Kidney Disease Worldwide.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Jan;17(1):8-10. doi: 10.2215/CJN.14861121. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34980676 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jager KJ, Kovesdy C, Langham R, Rosenberg M, Jha V, Zoccali C: A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Kidney Int 96: 1048–1050, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY, Yang CW: Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382: 260–272, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V, Neal B, Patrice HM, Okpechi I, Zhao MH, Lv J, Garg AX, Knight J, Rodgers A, Gallagher M, Kotwal S, Cass A, Perkovic V: Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review. Lancet 385: 1975–1982, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Couser WG, Remuzzi G, Mendis S, Tonelli M: The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int 80: 1258–1270, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

