Kidney Transplantation From Deceased Donors With Bloodstream Infection: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- PMID: 34981680
- PMCID: PMC8723893
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e4
Kidney Transplantation From Deceased Donors With Bloodstream Infection: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background: The use of organs from donors with infection is limited because of the possibility of transmission. We aimed to investigate the transmission after deceased donor transplantation with bloodstream infection (BSI).
Methods: A retrospective study of patients undergoing kidney or pancreas transplantation at five tertiary centers in Korea from January 2009 and November 2019 was performed. We analyzed the outcomes after transplantation from deceased donors with BSI.
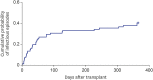
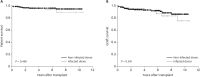
Results: Eighty-six recipients received transplantation from 69 donors with BSI. The most common isolated pathogens from donors were Gram-positive bacteria (72.0%), followed by Gram-negative bacteria (22.7%), and fungi (5.3%). Appropriate antimicrobial agents were used in 47.8% of donors before transplantation. Transmission occurred only in 1 of 83 recipients (1.2%) from bacteremic donors and 1 of 6 recipients (16.7%) from fungemic donors. One-year patient and graft survival was 97.5%and 96.3%, respectively. There was no significant difference in graft and patient survival between patients who received organs from infected donors and noninfected donors.
Conclusion: Using organs from donors with bacteremia seems to be a safe option with low transmission risk. The overall prognosis of using organs from donors with BSI is favorable.
Keywords: Bacteremia; Fungi; Kidney Transplantation; Retrospective Studies.
© 2022 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Ison MG, Hager J, Blumberg E, Burdick J, Carney K, Cutler J, et al. Donor-derived disease transmission events in the United States: data reviewed by the OPTN/UNOS Disease Transmission Advisory Committee. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(8):1929–1935. - PubMed
-
- Caballero F, Lopez-Navidad A, Perea M, Cabrer C, Guirado L, Solà R. Successful liver and kidney transplantation from cadaveric donors with left-sided bacterial endocarditis. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(4 Pt 1):781–787. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J, Michowiz R, Ashkenazi T, Pitlik S, Singer P. Successful organ transplantation from donors with Acinetobacter baumannii septic shock. Transplantation. 2006;81(6):853–855. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg E, Bishara J, Lev S, Singer P, Cohen J. Organ transplantation from a donor colonized with a multidrug-resistant organism: a case report. Transpl Infect Dis. 2012;14(3):296–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical