The CD6/ALCAM pathway promotes lupus nephritis via T cell-mediated responses
- PMID: 34981775
- PMCID: PMC8718154
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI147334
The CD6/ALCAM pathway promotes lupus nephritis via T cell-mediated responses
Abstract
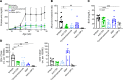
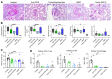
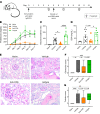
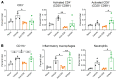
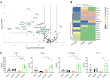
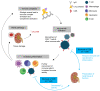
T cells are central to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis (LN), a common complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). CD6 and its ligand, activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), are involved in T cell activation and trafficking. Previously, we showed that soluble ALCAM is increased in urine (uALCAM) of patients with LN, suggesting that this pathway contributes to disease. To investigate, uALCAM was examined in 1038 patients with SLE and LN from 5 ethnically diverse cohorts; CD6 and ALCAM expression was assessed in LN kidney cells; and disease contribution was tested via antibody blockade of CD6 in murine models of SLE and acute glomerulonephritis. Extended cohort analysis offered resounding validation of uALCAM as a biomarker that distinguishes active renal involvement in SLE, irrespective of ethnicity. ALCAM was expressed by renal structural cells whereas CD6 expression was exclusive to T cells, with elevated numbers of CD6+ and ALCAM+ cells in patients with LN. CD6 blockade in models of spontaneous lupus and immune-complex glomerulonephritis revealed significant decreases in immune cells, inflammatory markers, and disease measures. Our data demonstrate the contribution of the CD6/ALCAM pathway to LN and SLE, supporting its use as a disease biomarker and therapeutic target.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Lupus.
Figures
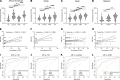
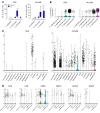
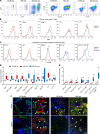
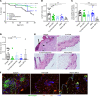
Comment in
-
CD6 is a therapeutic target for LN.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Mar;18(3):125. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00756-w. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35136210 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UH2 AR067685/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM2 AR067678/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR074096/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067688/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067689/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067690/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067694/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069572/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067679/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067676/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067691/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

