Establishment of developmental gene silencing by ordered polycomb complex recruitment in early zebrafish embryos
- PMID: 34982026
- PMCID: PMC8769650
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67738
Establishment of developmental gene silencing by ordered polycomb complex recruitment in early zebrafish embryos
Abstract
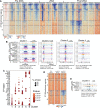
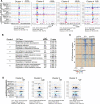
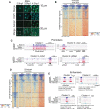
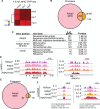
Vertebrate embryos achieve developmental competency during zygotic genome activation (ZGA) by establishing chromatin states that silence yet poise developmental genes for subsequent lineage-specific activation. Here, we reveal the order of chromatin states in establishing developmental gene poising in preZGA zebrafish embryos. Poising is established at promoters and enhancers that initially contain open/permissive chromatin with 'Placeholder' nucleosomes (bearing H2A.Z, H3K4me1, and H3K27ac), and DNA hypomethylation. Silencing is initiated by the recruitment of polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1), and H2Aub1 deposition by catalytic Rnf2 during preZGA and ZGA stages. During postZGA, H2Aub1 enables Aebp2-containing PRC2 recruitment and H3K27me3 deposition. Notably, preventing H2Aub1 (via Rnf2 inhibition) eliminates recruitment of Aebp2-PRC2 and H3K27me3, and elicits transcriptional upregulation of certain developmental genes during ZGA. However, upregulation is independent of H3K27me3 - establishing H2Aub1 as the critical silencing modification at ZGA. Taken together, we reveal the logic and mechanism for establishing poised/silent developmental genes in early vertebrate embryos.
Keywords: Placeholder; chromatin; chromosomes; development; developmental biology; gene expression; polycomb; ubiquitylation; zebrafish; zygotic genome activation.
© 2022, Hickey et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GH, CW, XN, YG, MT, PM, BC No competing interests declared
Figures




References
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, Jaenisch R, Wagschal A, Feil R, Schreiber SL, Lander ES. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blackledge NP, Farcas AM, Kondo T, King HW, McGouran JF, Hanssen LLP, Ito S, Cooper S, Kondo K, Koseki Y, Ishikura T, Long HK, Sheahan TW, Brockdorff N, Kessler BM, Koseki H, Klose RJ. Variant PRC1 complex-dependent H2A ubiquitylation drives PRC2 recruitment and polycomb domain formation. Cell. 2014;157:1445–1459. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- SRA/SRP020008
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

