RNA polymerase II pausing in development: orchestrating transcription
- PMID: 34982944
- PMCID: PMC8727152
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.210220
RNA polymerase II pausing in development: orchestrating transcription
Abstract
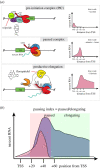
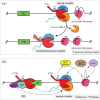
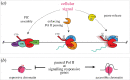
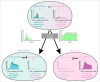
The coordinated regulation of transcriptional networks underpins cellular identity and developmental progression. RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing (Pol II pausing) is a prevalent mechanism by which cells can control and synchronize transcription. Pol II pausing regulates the productive elongation step of transcription at key genes downstream of a variety of signalling pathways, such as FGF and Nodal. Recent advances in our understanding of the Pol II pausing machinery and its role in transcription call for an assessment of these findings within the context of development. In this review, we discuss our current understanding of the molecular basis of Pol II pausing and its function during organismal development. By critically assessing the tools used to study this process we conclude that combining recently developed genomics approaches with refined perturbation systems has the potential to expand our understanding of Pol II pausing mechanistically and functionally in the context of development and beyond.
Keywords: Pol II pausing; development; embryonic stem cells; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
A.A., V.G. and A.-K.H. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
