Disruption of the IL-33-ST2-AKT signaling axis impairs neurodevelopment by inhibiting microglial metabolic adaptation and phagocytic function
- PMID: 34982959
- PMCID: PMC9074730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.12.001
Disruption of the IL-33-ST2-AKT signaling axis impairs neurodevelopment by inhibiting microglial metabolic adaptation and phagocytic function
Abstract
To accommodate the changing needs of the developing brain, microglia must undergo substantial morphological, phenotypic, and functional reprogramming. Here, we examined whether cellular metabolism regulates microglial function during neurodevelopment. Microglial mitochondria bioenergetics correlated with and were functionally coupled to phagocytic activity in the developing brain. Transcriptional profiling of microglia with diverse metabolic profiles revealed an activation signature wherein the interleukin (IL)-33 signaling axis is associated with phagocytic activity. Genetic perturbation of IL-33 or its receptor ST2 led to microglial dystrophy, impaired synaptic function, and behavioral abnormalities. Conditional deletion of Il33 from astrocytes or Il1rl1, encoding ST2, in microglia increased susceptibility to seizures. Mechanistically, IL-33 promoted mitochondrial activity and phagocytosis in an AKT-dependent manner. Mitochondrial metabolism and AKT activity were temporally regulated in vivo. Thus, a microglia-astrocyte circuit mediated by the IL-33-ST2-AKT signaling axis supports microglial metabolic adaptation and phagocytic function during early development, with implications for neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: IL-33; bioenergenetics; microglia; neurodevelopment; phagocytosis; seizure; synapse.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests V.K.K. has an ownership interest and is a member of the SAB of Celsius Therapeutics and Tizona Therapeutics. V.K.K.’s interests were reviewed and managed by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Partners Healthcare in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. A.R. is a co-founder and equity holder of Celsius Therapeutics, equity holder of Immunitas, and, until August 2020, a SAB member of Thermo Fisher Scientific, Syros Pharmaceuticals, Neogene Therapeutics, and Asimov. A.R. is an employee of Genentech. O.R.-R. is an employee of Genentech. O.R.-R. is a co-inventor on patent applications filed by the Broad related to single cell genomics. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

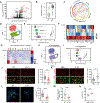

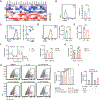


References
-
- Bouffi C, Rochman M, Zust CB, Stucke EM, Kartashov A, Fulkerson PC, Barski A, and Rothenberg ME (2013). IL-33 markedly activates murine eosinophils by an NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism differentially dependent upon an IL-4-driven autoinflammatory loop. J Immunol 191, 4317–4325. 10.4049/jimmunol.1301465. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

