Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review
- PMID: 34983359
- PMCID: PMC8903524
- DOI: 10.1186/s12245-021-00399-w
Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review
Abstract
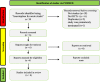
Introduction: Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) with alteplase is the currently approved therapy for patients who present within 4.5 h of symptom onset and meet criteria. Recently, there has been interest in the thrombolytic tenecteplase, a modified version of alteplase, due to its lower cost, ease of administration, and studies reporting better outcomes when compared to alteplase. This systematic review compares the efficacy of tenecteplase vs. alteplase with regard to three outcomes: (1) rate of symptomatic hemorrhage, (2) functional outcome at 90 days, and (3) reperfusion grade after thrombectomy to compare the efficacy of both thrombolytics in AIS METHODS: The search was conducted in August 2021 in PubMed, filtered for randomized controlled trials, and studies in English. The main search term was "tenecteplase for acute stroke."
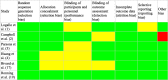
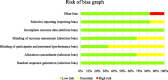
Results: A total of 6 randomized clinical trials including 1675 patients with AIS was included. No one's study compared alteplase to tenecteplase with all three outcomes after acute ischemic stroke; however, by using a combination of the results, this systematic review summarizes whether tenecteplase outperforms alteplase.
Conclusions: The available evidence suggests that tenecteplase appears to be a better thrombolytic agent for acute ischemic stroke when compared to alteplase.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(24):1581–7. 10.1056/NEJM199512143332401. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources