Group problem management plus (PM+) to decrease psychological distress among Syrian refugees in Turkey: a pilot randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 34983461
- PMCID: PMC8728921
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-021-03645-w
Group problem management plus (PM+) to decrease psychological distress among Syrian refugees in Turkey: a pilot randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Syrian refugees resettled in Turkey show a high prevalence of symptoms of mental disorders. Problem Management Plus (PM+) is an effective psychological intervention delivered by non-specialist health care providers which has shown to decrease psychological distress among people exposed to adversity. In this single-blind pilot randomised controlled trial, we examined the methodological trial procedures of Group PM+ (gPM+) among Syrian refugees with psychological distress in Istanbul, Turkey, and assessed feasibility, acceptability, perceived impact and the potential cost-effectiveness of the intervention.
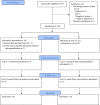
Methods: Refugees with psychological distress (Kessler Psychological Distress Scale, K10 > 15) and impaired psychosocial functioning (World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule, WHODAS 2.0 > 16) were recruited from the community and randomised to either gPM+ and enhanced care as usual (E-CAU) (n = 24) or E-CAU only (n = 22). gPM+ comprised of five weekly group sessions with eight to ten participants per group. Acceptability and feasibility of the intervention were assessed through semi-structured interviews. The primary outcome at 3-month follow-up was symptoms of depression and anxiety (Hopkins Symptoms Checklist-25). Psychosocial functioning (WHODAS 2.0), symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder and self-identified problems (Psychological Outcomes Profiles, PSYCHLOPS) were included as secondary outcomes. A modified version of the Client Service Receipt Inventory was used to document changes in the costs of health service utilisation as well as productivity losses.
Results: There were no barriers experienced in recruiting study participants and in randomising them into the respective study arms. Retention in gPM+ was high (75%). Qualitative analyses of the interviews with the participants showed that Syrian refugees had a positive view on the content, implementation and format of gPM+. No adverse events were reported during the implementation. The study was not powered to detect an effect. No significant difference between gPM+ and E-CAU group on primary and secondary outcome measures, or in economic impacts were found.
Conclusions: gPM+ delivered by non-specialist peer providers seemed to be an acceptable, feasible and safe intervention for Syrian refugees in Turkey with elevated levels of psychological distress. This pilot RCT sets the stage for a fully powered RCT.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT03567083 ; date: 25/06/2018.
Keywords: Common mental health problems; Feasibility; Group intervention; Pilot; Randomised controlled trial; Refugees; Task sharing.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- United Nations high commissioner for refugees. Figures at a Glance 2020. https://www.unhcr.org/figures-at-a-glance.html. Accessed 24 Jun 2020.
-
- UNHCR. Operational Update October 2020. p. 2020.
-
- UNHCR. Syria regional refugee response. Opetaional Portal Refugee Situations. 2020; https://data2.unhcr.org/en/situations/syria#_ga=2.218907088.858158040.15.... Accessed 24 Jun 2020.
-
- Alpak G, Unal A, Bulbul F, Sagaltici E, Bez Y, Altindag A, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder among Syrian refugees in Turkey: a cross-sectional study. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials