Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 therapy and SARS-CoV-2 detection
- PMID: 34983527
- PMCID: PMC8724751
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-021-00784-w
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 therapy and SARS-CoV-2 detection
Abstract
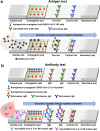
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is an exceptional public health crisis that demands the timely creation of new therapeutics and viral detection. Owing to their high specificity and reliability, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have emerged as powerful tools to treat and detect numerous diseases. Hence, many researchers have begun to urgently develop Ab-based kits for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Ab drugs for use as COVID-19 therapeutic agents. The detailed structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is known, and since this protein is key for viral infection, its receptor-binding domain (RBD) has become a major target for therapeutic Ab development. Because SARS-CoV-2 is an RNA virus with a high mutation rate, especially under the selective pressure of aggressively deployed prophylactic vaccines and neutralizing Abs, the use of Ab cocktails is expected to be an important strategy for effective COVID-19 treatment. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 infection may stimulate an overactive immune response, resulting in a cytokine storm that drives severe disease progression. Abs to combat cytokine storms have also been under intense development as treatments for COVID-19. In addition to their use as drugs, Abs are currently being utilized in SARS-CoV-2 detection tests, including antigen and immunoglobulin tests. Such Ab-based detection tests are crucial surveillance tools that can be used to prevent the spread of COVID-19. Herein, we highlight some key points regarding mAb-based detection tests and treatments for the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: Angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2); Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); Cytokine storm; Receptor binding motif (RBM); Receptor-binding domain (RBD); Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2); Spike; Therapeutic antibody; Viral detection.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures




References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed 23 Mar 2021.
-
- Struyf T, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Takwoingi Y, Davenport C, Leeflang MM, Spijker R, Hooft L, Emperador D, Dittrich S, Domen J, Horn SRA, Van den Bruel A, Cochrane C-DTAG. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;7:13665. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

