Prone position plexopathy: an avoidable complication of prone positioning for COVID-19 pneumonitis?
- PMID: 34983806
- PMCID: PMC8728371
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-243798
Prone position plexopathy: an avoidable complication of prone positioning for COVID-19 pneumonitis?
Abstract
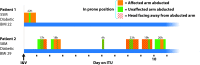
Prone positioning is a mainstay of management for those presenting to the intensive care unit with moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19. While this is a necessary and life-saving intervention in selected patients, careful positioning and meticulous care are required to prevent compression and traction of the brachial plexus, and resultant brachial plexopathy. We describe two patients who developed a brachial plexus injury while undergoing prone positioning for management of COVID-19 pneumonitis. Both patients were diabetic and underwent prolonged periods in the prone position during which the plexopathy affected arm was abducted for 19 and 55 hours, respectively. We discuss strategies to reduce the risk of this rare but potentially disabling complication of prone positioning.
Keywords: COVID-19; adult intensive care; neurological injury; peripheral nerve disease.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
