Engineering synthetic RNA devices for cell control
- PMID: 34983970
- PMCID: PMC9554294
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-021-00436-7
Engineering synthetic RNA devices for cell control
Abstract
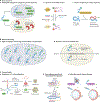
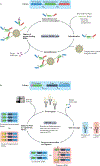
The versatility of RNA in sensing and interacting with small molecules, proteins and other nucleic acids while encoding genetic instructions for protein translation makes it a powerful substrate for engineering biological systems. RNA devices integrate cellular information sensing, processing and actuation of specific signals into defined functions and have yielded programmable biological systems and novel therapeutics of increasing sophistication. However, challenges centred on expanding the range of analytes that can be sensed and adding new mechanisms of action have hindered the full realization of the field's promise. Here, we describe recent advances that address these limitations and point to a significant maturation of synthetic RNA-based devices.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nshogozabahizi JC, Aubrey KL, Ross JA & Thakor N Applications and limitations of regulatory RNA elements in synthetic biology and biotechnology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 127, 968–984 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Kim J & Franco E RNA nanotechnology in synthetic biology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 63, 135–141 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Park SV et al. Catalytic RNA, ribozyme, and its applications in synthetic biology. Biotechnol. Adv. 37, 107452 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

