Complete Response to PD-1 Inhibitor in Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Post-Progression on Bi-Specific Antibody Conjugated CIK Cell Treatment: A Report of Two Cases
- PMID: 34984004
- PMCID: PMC8702989
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S333604
Complete Response to PD-1 Inhibitor in Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Post-Progression on Bi-Specific Antibody Conjugated CIK Cell Treatment: A Report of Two Cases
Abstract
Background: Programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have produced encouraging results in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells treatment can specifically identify tumor-associated antigens and has encouraging preliminary efficacy for HCC. This study reported two cases of HCC patients achieved complete response (CR) by anti-PD-1 antibody therapy post-progression on bi-specific antibody conjugated CIK immunotherapy.
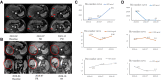
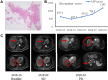
Case presentation: Case one, a 75-year-old male, was diagnosed with the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) in October 2017. After interventional, CIK, ablation and other comprehensive therapy, ICC was gradually cured. When new occurrence of HCC, he was treated with anti-PD-1 antibody therapy and achieved CR. Case two, a 65-year-old female, was diagnosed with HCC in July 2016. After progression on several ablation treatments, she received 8 cycles of CIK treatment and achieved stable disease (SD). After disease progressed on CIK treatment, she received 4 cycles of anti-PD-1 antibody therapy, finally achieved CR.
Conclusion: Anti-PD-1 antibody therapy after prior progression on bi-specific antibody conjugated CIK immunotherapy may be efficacy and safety for HCC patients.
Keywords: complete response; cytokine-induced killer; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver; programmed cell death-1.
© 2021 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adjuvant cytokine-induced killer cells with minimally invasive therapies augmented therapeutic efficacy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Ther. 2020;16(7):1603-1610. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_962_19. J Cancer Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33565506
-
High number of PD-1 positive intratumoural lymphocytes predicts survival benefit of cytokine-induced killer cells for hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Liver Int. 2018 Aug;38(8):1449-1458. doi: 10.1111/liv.13697. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Liver Int. 2018. PMID: 29356308 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker for cytokine-induced killer cell immunotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncoimmunology. 2016 May 31;5(7):e1176653. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1176653. eCollection 2016 Jul. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 27622026 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Improve the Antitumor Effect of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 26;12:783236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783236. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical benefits of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hepatol Int. 2020 Sep;14(5):765-775. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10064-8. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Hepatol Int. 2020. PMID: 32572818
Cited by
-
Exploration of the role of immune cells and cell therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1569150. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1569150. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40308592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of MUC1-Overexpressing Tumors by a Novel MUC1/CD3 Bispecific Antibody.Antibodies (Basel). 2023 Jul 13;12(3):47. doi: 10.3390/antib12030047. Antibodies (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37489369 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial heterogeneity of the hepatocellular carcinoma microenvironment determines the efficacy of immunotherapy.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 7;16(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01747-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39775241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination treatment of pembrolizumab with DC-CIK cell therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2023 Sep 1;13(3):57-62. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1414. eCollection 2023. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2023. PMID: 37937058 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends of cellular immunotherapy for primary liver cancer: A bibliometric analysis.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2426869. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2426869. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39538378 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

