Family History, Consanguinity and Other Risk Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Prediabetes and Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus in Overweight and Obese Yemeni Adults
- PMID: 34984017
- PMCID: PMC8709553
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S344440
Family History, Consanguinity and Other Risk Factors Affecting the Prevalence of Prediabetes and Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus in Overweight and Obese Yemeni Adults
Abstract
Objective: Overweight and obese adults are at high risk for developing prediabetes and diabetes. The aim of this study was to measure the prevalence of prediabetes (pre-DM) and diabetes (DM) among Yemeni adults who were overweight or obese and had first-degree relatives with DM, consanguinity and other risk factors.
Patients and methods: This cross-sectional study included 612 adults, all with a BMI≥25 kg/m2. BMI, blood pressure (BP) and waist circumference (WC) were measured in the clinic. Fasting blood glucose (FBG) was collected for all subjects. The patients either had first-degree relatives with diabetes or not, and the subjects answered a questionnaire regarding the consanguinity of their parents, exercise, khat chewing, smoking, and eating vegetables and fruits daily.
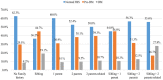
Results: Of the 612 study participants (32% males and 68% females) aged 20-70 years old, 429 (70.1%) had a family history (FM) of DM ± consanguinity of parents, and 183 (29.9%) had no FM of diabetes. Multivariate analysis showed significant risk in those with class III obesity for pre-DM (AOR 3.10 95% CI 1.56-6.18 p value 0.001) and DM (AOR 3.35 95% CI 1.47-7.65 p value 0.004) and those who had siblings with DM had a risk for pre-DM (AOR 1.72 95% CI 1.09-2.71 p value 0.02) and DM (AOR 2.24 95% CI 1.25-4.0 p value 0.007). Khat chewing increased the risk for pre-DM (AOR 1.61 95% CI 1.04-2.48 p value 0.032) and for DM (AOR 2.09 95% CI 1.14-3.82 p value 0.017). Having consanguineous parents plus siblings with DM were associated with a higher risk of DM (p value 0.031).
Conclusion: There is a high prevalence of pre-DM and undiagnosed DM among overweight and obese Yemeni individuals. Class III obesity, having siblings with DM, chewing khat, and having consanguineous parents plus siblings with DM all increased the risk. This group should be screened at an early age for early detection of pre-DM and DM.
Keywords: Yemen; consanguinity; diabetes; khat-chewing; obese; overweight; prediabetes; prevalence.
© 2021 Al-Sharafi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Alharbi KK, Abudawood M, Khan IA. Amino-acid amendment of Arginine-325-Tryptophan in rs13266634 genetic polymorphism studies of the SLC30A8 gene with type 2 diabetes-mellitus patients featuring a positive family history in the Saudi population. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2021;33(1):101258. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2020.101258 - DOI
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

