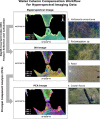
Water column compensation workflow for hyperspectral imaging data
- PMID: 34984174
- PMCID: PMC8693006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2021.101601
Water column compensation workflow for hyperspectral imaging data
Abstract
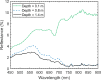
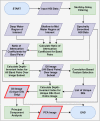
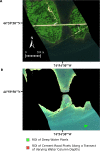
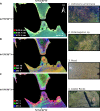
Our article describes a data processing workflow for hyperspectral imaging data to compensate for the water column in shallow, clear to moderate optical water types. We provide a MATLAB script that can be readily used to implement the described workflow. We break down each code segment of this script so that it is more approachable for use and modification by end users and data providers. The workflow initially implements the method for water column compensation described in Lyzenga (1978) and Lyzenga (1981), generating depth invariant indices from spectral band pairs. Given the high dimensionality of hyperspectral imaging data, an overwhelming number of depth invariant indices are generated in the workflow. As such, a correlation based feature selection methodology is applied to remove redundant depth invariant indices. In a post-processing step, a principal component transformation is applied, extracting features that account for a substantial amount of the variance from the non-redundant depth invariant indices while reducing dimensionality. To fully showcase the developed methodology and its potential for extracting bottom type information, we provide an example output of the water column compensation workflow using hyperspectral imaging data collected over the coast of Philpott's Island in Long Sault Parkway provincial park, Ontario, Canada.•Workflow calculates depth invariant indices for hyperspectral imaging data to compensate for the water column in shallow, clear to moderate optical water types.•The applied principal component transformation generates features that account for a substantial amount of the variance from the depth invariant indices while reducing dimensionality.•The output (both depth invariant index image and principal component image) allows for the analysis of bottom type in shallow, clear to moderate optical water types.
Keywords: Depth invariant index (DII); Hyperspectral imaging; Principal component analysis (PCA); Water column compensation.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Amran M.A., Rappe R.A. Estimation of seagrass coverage by depth invariant indices on quickbird imagery. Biotropia. 2010;17:42–50.
-
- Dierssen H.M., Ackleson S.G., Joyce K.E., Hestir E.L., Castagna A., Lavender S., McManus M.A. Living up to the hype of hyperspectral aquatic remote sensing: science, resources and outlook. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021;9
-
- Eismann M.T. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. SPIE; Bellingham: 2012. 1.1 Hyperspectral remote sensing.
-
- El Mahrad B., Newton A., Icely J.D., Kacimi I., Abalansa S., Snoussi M. Contribution of remote sensing technologies to a holistic coastal and marine environmental management framework: a review. Remote Sens. 2020;12:2313.
-
- Gordon H.R., McCluney W.R. Estimation of the depth of sunlight penetration in the sea for remote sensing. Appl. Opt. 1975;14:413–416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

