On-chip magnetophoretic capture in a model of malaria-infected red blood cells
- PMID: 34984673
- PMCID: PMC9306751
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.28030
On-chip magnetophoretic capture in a model of malaria-infected red blood cells
Abstract
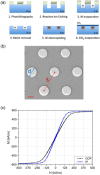
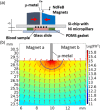
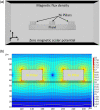
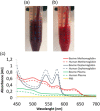
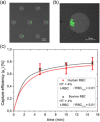
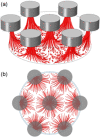
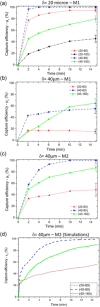
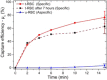
The search for new rapid diagnostic tests for malaria is a priority for developing an efficient strategy to fight this endemic disease, which affects more than 3 billion people worldwide. In this study, we characterize systematically an easy-to-operate lab-on-chip, designed for the magnetophoretic capture of malaria-infected red blood cells (RBCs). The method relies on the positive magnetic susceptibility of infected RBCs with respect to blood plasma. A matrix of nickel posts fabricated in a silicon chip placed face down is aimed at attracting infected cells, while healthy cells sediment on a glass slide under the action of gravity. Using a model of infected RBCs, that is, erythrocytes with methemoglobin, we obtained a capture efficiency of about 70% after 10 min in static conditions. By proper agitation, the capture efficiency reached 85% after just 5 min. Sample preparation requires only a 1:10 volume dilution of whole blood, previously treated with heparin, in a phosphate-buffered solution. Nonspecific attraction of untreated RBCs was not observed in the same time interval.
Keywords: lab-on-a-chip; magnetorphoretic separation; malaria.
© 2022 The Authors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


References
-
- Bertacco, R. , Petti, D. , Ferrari, G. , Albisetti, E. , & Giacometti, M. (2017). Device and method for the quantification of cellular and non‐cellular blood components. Ital. Pat. n. 102017000082112.
-
- Bertacco, R. , Fiore, G. B. , Ferrari, G. , Giacometti, M. , Milesi, F. , Coppadoro, L. P. & Giuliani, E. (2019). Apparato per la quantificazione di componenti biologiche disperse in un fluido. Ital. Pat. n. 102019000000821.
-
- Blue Martin, A. , Wu, W.‐T. , Kameneva, M. V. , & Antaki, J. F. (2017). Development of a high‐throughput magnetic separation device for malaria‐infected erythrocytes. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 45, 2888–2898. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10439-017-1925-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bottiger, L. E. , & Svedberg, C. A. (1967). Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and age. BMJ, 2, 85–87. https://www.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmj.2.5544.85 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen, J. M. , Smith, D. L. , Cotter, C. , Ward, A. , Yamey, G. , Sabot, O. J. , & Moonen, B. (2012). Malaria resurgence: A systematic review and assessment of its causes. Malaria Journal, 11, 122. https://malariajournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2875-11-122 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

