Cavefish cope with environmental hypoxia by developing more erythrocytes and overexpression of hypoxia-inducible genes
- PMID: 34984980
- PMCID: PMC8765751
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69109
Cavefish cope with environmental hypoxia by developing more erythrocytes and overexpression of hypoxia-inducible genes
Abstract
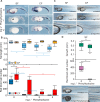
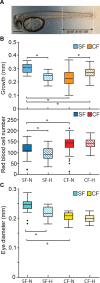
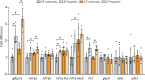
Dark caves lacking primary productivity can expose subterranean animals to hypoxia. We used the surface-dwelling (surface fish) and cave-dwelling (cavefish) morphs of Astyanax mexicanus as a model for understanding the mechanisms of hypoxia tolerance in the cave environment. Primitive hematopoiesis, which is restricted to the posterior lateral mesoderm in other teleosts, also occurs in the anterior lateral mesoderm in Astyanax, potentially pre-adapting surface fish for hypoxic cave colonization. Cavefish have enlarged both hematopoietic domains and develop more erythrocytes than surface fish, which are required for normal development in both morphs. Laboratory-induced hypoxia suppresses growth in surface fish but not in cavefish. Both morphs respond to hypoxia by overexpressing hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (hif1) pathway genes, and some hif1 genes are constitutively upregulated in normoxic cavefish to similar levels as in hypoxic surface fish. We conclude that cavefish cope with hypoxia by increasing erythrocyte development and constitutive hif1 gene overexpression.
Keywords: cavefish; developmental biology; erythrocytes; evolution; evolutionary biology; hematopoiesis; hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factor genes.
© 2022, van der Weele and Jeffery.
Conflict of interest statement
Cv, WJ No competing interests declared
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-sonic hedgehog axis as a driver of primitive hematopoiesis development and evolution in cavefish.Dev Biol. 2024 Dec;516:138-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.08.008. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39173434
-
Alterations to cavefish red blood cells provide evidence of adaptation to reduced subterranean oxygen.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 8;12(1):3735. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07619-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35260642 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic plasticity as a mechanism of cave colonization and adaptation.Elife. 2020 Apr 21;9:e51830. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51830. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32314737 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Genetics of the Cavefish Astyanax mexicanus.Adv Genet. 2016;95:117-59. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Adv Genet. 2016. PMID: 27503356 Review.
-
Subterranean life: Behavior, metabolic, and some other adaptations of Astyanax cavefish.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2020 Nov;334(7-8):463-473. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.22948. Epub 2020 Apr 28. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2020. PMID: 32346998 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia Affects HIF-1/LDH-A Signaling Pathway by Methylation Modification and Transcriptional Regulation in Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus).Biology (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;11(8):1233. doi: 10.3390/biology11081233. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009861 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-sonic hedgehog axis as a driver of primitive hematopoiesis development and evolution in cavefish.Dev Biol. 2024 Dec;516:138-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2024.08.008. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39173434
-
A practical guide for the husbandry of cave and surface invertebrates as the first step in establishing new model organisms.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 4;19(4):e0300962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300962. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38573919 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals hypoxic response key genes and modules as well as adaptive mechanism of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) gill under hypoxic stress.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 5;16:1543605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543605. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39975546 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-seq analysis of blood from cave- and surface-dwelling Astyanax morphs reveal diverse transcriptomic responses to normoxic rearing.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 17;16:1617136. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1617136. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40746987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birnie-Gauvin K, Costantini D, Cooke SJ, Willmore WG. A comparative and evolutionary approach to oxidative stress in fish: A review. Fish and Fisheries. 2017;18:928–942. doi: 10.1111/faf.12215. - DOI
-
- Bishop RE, Torres JJ, Kakuk B. Life in the Hypoxic and Anoxic Zones: Metabolism and Proximate Composition of Caribbean Troglobitic Crustaceans with Observations on the Water Chemistry of Two Anchialine Caves. Journal of Crustacean Biology. 2004;24:379–392. doi: 10.1651/C-2459. - DOI
-
- Boggs T, Gross J. Reduced Oxygen as an Environmental Pressure in the Evolution of the Blind Mexican Cavefish. Diversity. 2021;13:26. doi: 10.3390/d13010026. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

