Circular BANP knockdown inhibits the malignant progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation
- PMID: 34985013
- PMCID: PMC9532039
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001822
Circular BANP knockdown inhibits the malignant progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are endogenous non-coding RNAs, some of which have pathological roles. The current study aimed to explore the role of circRNA BTG3-associated nuclear protein (circ-BANP) binding with let-7f-5p and its regulation of the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway in residual hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after insufficient radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Methods: Circ-BANP, let-7f-5p, and TLR4 expressions in HCC samples were assessed using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blotting. Bioinformatics prediction, RNA pull-down assay, and dual luciferase reporter gene assay were used to analyze the relationships among circ-BANP, let-7f-5p, and TLR4. Huh7 cells were used to generate an in vitro model of residual HCC, defined as Huh7-H cells, which were transfected with either a plasmid or the sequence of circ-BANP, let-7f-5p, or TLR4. Expression of circ-BANP, let-7f-5p, and TLR4 mRNA was determined by RT-qPCR. TLR4, STAT3, p-STAT3, vascular endothelial growth factor A, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2, and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT)-related factors proteins were determined by Western blotting. Cell proliferation was determined by cell counting kit-8 and 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assay and cell migration and invasion by Transwell assay. Animal studies were performed by inducing xenograft tumors in nude mice.
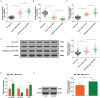
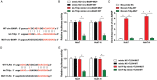
Results: Circ-BANP and TLR4 mRNAs were upregulated in HCC tissues (the fold change for circ-BANP was 1.958 and that for TLR4 was 1.736 relative to para-tumors) and expression further increased following insufficient RFA (fold change for circ-BANP was 2.407 and that of TLR4 was 2.224 relative to para-tumors). Expression of let-7f-5p showed an opposite tendency (fold change for let-7f-5p in HCC tissues was 0.491 and that in tumors after insufficient RFA was 0.300 relative to para-tumors). Competitive binding of circ-BANP to let-7f-5p was demonstrated and TLR4 was identified as a target of let-7f-5p (P < 0.01). Knockdown of circ-BANP or elevation of let-7f-5p expression inhibited the TLR4/STAT3 signaling pathway, proliferation, invasion, migration, angiogenesis, and EMT in Huh7 and Huh7-H cells (P < 0.01). The effects induced by circ-BANP knockdown were reversed by let-7f-5p inhibition. Overexpression of TLR4 reversed the impact of let-7f-5p upregulation on the cells (P < 0.01). Silencing of circ-BANP inhibited the in vivo growth of residual HCC cells after insufficient RFA (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Knockdown of circ-BANP upregulated let-7f-5p to inhibit proliferation, migration, and EMT formation in residual HCC remaining after insufficient RFA. Effects occur via regulation of the TLR4/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2022 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Chen S, Cao Q, Wen W, Wang H. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and opportunities. Cancer Lett 2019; 460:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.114428. - PubMed
-
- Niu ZS, Niu XJ, Wang WH. Rle of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical relevance. Future Oncol 2019; 15:653–662. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0528. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

