Catestatin induces glycogenesis by stimulating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT pathway
- PMID: 34985191
- PMCID: PMC10754386
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.13775
Catestatin induces glycogenesis by stimulating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT pathway
Abstract
Aim: Defects in hepatic glycogen synthesis contribute to post-prandial hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetic patients. Chromogranin A (CgA) peptide Catestatin (CST: hCgA352-372 ) improves glucose tolerance in insulin-resistant mice. Here, we seek to determine whether CST induces hepatic glycogen synthesis.
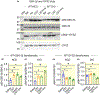
Methods: We determined liver glycogen, glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG) and glycogen synthase (GYS2) activities; plasma insulin, glucagon, noradrenaline and adrenaline levels in wild-type (WT) as well as in CST knockout (CST-KO) mice; glycogen synthesis and glycogenolysis in primary hepatocytes. We also analysed phosphorylation signals of insulin receptor (IR), insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase-1 (PDK-1), GYS2, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), AKT (a kinase in AKR mouse that produces Thymoma)/PKB (protein kinase B) and mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) by immunoblotting.
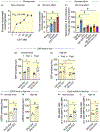
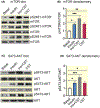
Results: CST stimulated glycogen accumulation in fed and fasted liver and in primary hepatocytes. CST reduced plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline levels. CST also directly stimulated glycogenesis and inhibited noradrenaline and adrenaline-induced glycogenolysis in hepatocytes. In addition, CST elevated the levels of UDPG and increased GYS2 activity. CST-KO mice had decreased liver glycogen that was restored by treatment with CST, reinforcing the crucial role of CST in hepatic glycogenesis. CST improved insulin signals downstream of IR and IRS-1 by enhancing phospho-AKT signals through the stimulation of PDK-1 and mTORC2 (mTOR Complex 2, rapamycin-insensitive complex) activities.
Conclusions: CST directly promotes the glycogenic pathway by (a) reducing glucose production, (b) increasing glycogen synthesis from UDPG, (c) reducing glycogenolysis and (d) enhancing downstream insulin signalling.
Keywords: catestatin; glucose-6-phosphate; glycogen; glycogen synthase; hyperglycaemia; phospho-AKT.
© 2022 Scandinavian Physiological Society. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures






Comment in
-
Hepatic glucose production and storage as a potential strategy for type 2 diabetes treatment - The effect of catestatin - "just another new kid in town?".Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022 May;235(1):e13808. doi: 10.1111/apha.13808. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35224867 No abstract available.
References
-
- Martin BC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Bergman RN, Soeldner JS, Kahn CR. Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet. 1992;340(8825):925–929. - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006;444(7121):840–846. - PubMed
-
- Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A. Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(6):2169–2180. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15019. - PubMed
-
- Menke A, Casagrande S, Geiss L, Cowie CC. Prevalence of and trends in diabetes among adults in the United States, 1988–2012. JAMA. 2015;314(10):1021–1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

