Restoration of mitophagy ameliorates cardiomyopathy in Barth syndrome
- PMID: 34985382
- PMCID: PMC9466615
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2021.2020979
Restoration of mitophagy ameliorates cardiomyopathy in Barth syndrome
Abstract
Barth syndrome (BTHS) is an X-linked genetic disorder caused by mutations in the TAFAZZIN/Taz gene which encodes a transacylase required for cardiolipin remodeling. Cardiolipin is a mitochondrial signature phospholipid that plays a pivotal role in maintaining mitochondrial membrane structure, respiration, mtDNA biogenesis, and mitophagy. Mutations in the TAFAZZIN gene deplete mature cardiolipin, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, dilated cardiomyopathy, and premature death in BTHS patients. Currently, there is no effective treatment for this debilitating condition. In this study, we showed that TAFAZZIN deficiency caused hyperactivation of MTORC1 signaling and defective mitophagy, leading to accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and dysfunctional mitochondria in the heart of Tafazzin knockdown mice, a rodent model of BTHS. Consequently, treatment of TAFAZZIN knockdown mice with rapamycin, a potent inhibitor of MTORC1, not only restored mitophagy, but also mitigated mitochondrial dysfunction and dilated cardiomyopathy. Taken together, these findings identify MTORC1 as a novel therapeutic target for BTHS, suggesting that pharmacological restoration of mitophagy may provide a novel treatment for BTHS.Abbreviations: BTHS: Barth syndrome; CCCP: carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone; CL: cardiolipin; EIF4EBP1/4E-BP1: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; KD: knockdown; KO: knockout; LAMP1: lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1; LV: left ventricle; MAP1LC3/LC3: microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; MEFs: mouse embryonic fibroblasts; MTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase complex 1; OCR: oxygen consumption rate; PE: phosphatidylethanolamine; PIK3C3/VPS34: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3; PINK1: PTEN induced putative kinase 1; PRKN/Parkin: parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; qRT-PCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; RPS6KB/S6K: ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta; SQSTM1/p62: sequestosome 1; TLCL: tetralinoleoyl cardiolipin; WT: wild-type.
Keywords: BTHS; MTORC1; TAFAZZIN; cardiolipin; mitophagy; rapamycin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
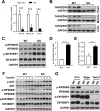
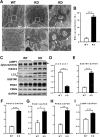
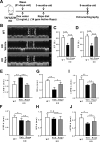
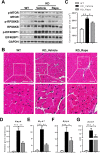


References
-
- Barth PG, Scholte HR, Berden JA, et al. An X-linked mitochondrial disease affecting cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and neutrophil leucocytes. J Neurol Sci. 1983. Dec;62(1–3):327–355. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Malhotra A, Ren M, et al. The enzymatic function of tafazzin. J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 22;281(51):39217–39224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
