The use of a single-piece bone flap for cranial reshaping in anterior craniosynostosis patients: clinical experience and a description of a novel technique
- PMID: 34985605
- PMCID: PMC8733119
- DOI: 10.1186/s40902-021-00332-4
The use of a single-piece bone flap for cranial reshaping in anterior craniosynostosis patients: clinical experience and a description of a novel technique
Abstract
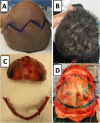
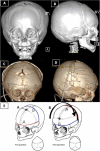
Background: Craniosynostosis is known as premature closure of one or more of the cranial sutures. Anterior craniosynostosis involves anterior plagiocephaly and trigonocephaly. One of the issues in anterior craniosynostosis skull reshaping is maintaining an aesthetically pleasing forehead curve. Therefore, in this article, we demonstrate our novel technique to use a single-piece bone flap for cranial reshaping of the anterior mold in patients diagnosed with anterior craniosynostosis. A retrospective record review of patients who underwent single piece bone flap cranial reshaping for correction of unicoronal synostosis (UCS) and metopic synostosis (MS) at an Academic Institute in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, between 2018 and 2020, was conducted.
Results: Six non-syndromic consecutive patients were included. Three of the patients had MS. The mean age at surgery was 11.16 months (range, 6-19 months). The average OR time was 315 min (range, 263-368 min). The average intraoperative blood loss was 225 ml (range, 100-400 ml). All patients had achieved acceptable functional and aesthetic results.
Conclusion: Our novel technique is an innovative and efficient reconstructive technique to simultaneously address MS and UCS and minimize intraoperative bleeding and surgery time. However, more studies with more cases are required.
Keywords: Bone flap; Cranial reshaping; Craniosynostosis; Plagiocephaly; Reconstruction; Trigonocephaly.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cranial orbital buttress technique for nonsyndromic unicoronal and metopic craniosynostosis.Neurosurg Focus. 2015 May;38(5):E4. doi: 10.3171/2015.2.FOCUS14844. Neurosurg Focus. 2015. PMID: 25929966
-
Anterior Cranial Vault Reconstruction With Distraction for Primary and Secondary Craniosynostosis Repair.J Craniofac Surg. 2019 Mar/Apr;30(2):e109-e112. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005011. J Craniofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30507890
-
[Non syndromic craniosynostosis].Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2016 Oct;61(5):389-407. doi: 10.1016/j.anplas.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2016. PMID: 27499256 French.
-
The metopic index: an anthropometric index for the quantitative assessment of trigonocephaly from metopic synostosis.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016 Sep;18(3):275-80. doi: 10.3171/2016.2.PEDS15524. Epub 2016 May 6. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27153376
-
Trigonocephaly: Long-term results after surgical correction of metopic suture synostosis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 May;28(5):625-635. doi: 10.17219/acem/90763. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 30712337
Cited by
-
A Comparative Study of the Effect of Low-Dose Epinephrine and Ketamine on Rapid-Sequence Endotracheal Intubation by the Priming Dose Method of Cisatracurium in Patients under General Anesthesia.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Jan 27;12:13. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_398_21. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 36926434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodriguez ED, Losee JE, Neligan PC (2012) Plastic Surgery E-Book: Volume 3: Craniofacial, Head and Neck SurgeryPediatric Plastic Surgery (Expert Consult-Online) (Vol. 3). Elsevier Health Sciences.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
