Activation of the MKK3-p38-MK2-ZFP36 Axis by Coronavirus Infection Restricts the Upregulation of AU-Rich Element-Containing Transcripts in Proinflammatory Responses
- PMID: 34985993
- PMCID: PMC8906397
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.02086-21
Activation of the MKK3-p38-MK2-ZFP36 Axis by Coronavirus Infection Restricts the Upregulation of AU-Rich Element-Containing Transcripts in Proinflammatory Responses
Abstract
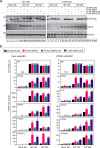
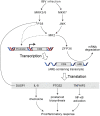
Coronavirus infections induce the expression of multiple proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. We have previously shown that in cells infected with gammacoronavirus infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and IL-8 were drastically upregulated, and the MAP kinase p38 and the integrated stress response pathways were implicated in this process. In this study, we report that coronavirus infection activates a negative regulatory loop that restricts the upregulation of a number of proinflammatory genes. As revealed by the initial transcriptomic and subsequent validation analyses, the anti-inflammatory adenine-uridine (AU)-rich element (ARE)-binding protein, zinc finger protein 36 (ZFP36), and its related family members were upregulated in cells infected with IBV and three other coronaviruses, alphacoronaviruses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E), and betacoronavirus HCoV-OC43, respectively. Characterization of the functional roles of ZFP36 during IBV infection demonstrated that ZFP36 promoted the degradation of transcripts coding for IL-6, IL-8, dual-specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1), prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) and TNF-α-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3), through binding to AREs in these transcripts. Consistently, knockdown and inhibition of JNK and p38 kinase activities reduced the expression of ZFP36, as well as the expression of IL-6 and IL-8. On the contrary, overexpression of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (MKK3) and MAPKAP kinase-2 (MK2), the upstream and downstream kinases of p38, respectively, increased the expression of ZFP36 and decreased the expression of IL-8. Taken together, this study reveals an important regulatory role of the MKK3-p38-MK2-ZFP36 axis in coronavirus infection-induced proinflammatory response. IMPORTANCE Excessive and uncontrolled induction and release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, the so-called cytokine release syndrome (CRS), would cause life-threatening complications and multiple organ failure in severe coronavirus infections, including severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and COVID-19. This study reveals that coronavirus infection also induces the expression of ZFP36, an anti-inflammatory ARE-binding protein, promoting the degradation of ARE-containing transcripts coding for IL-6 and IL-8 as well as a number of other proteins related to inflammatory response. Furthermore, the p38 MAP kinase, its upstream kinase MKK3 and downstream kinase MK2 were shown to play a regulatory role in upregulation of ZFP36 during coronavirus infection cycles. This MKK3-p38-MK2-ZFP36 axis would constitute a potential therapeutic target for severe coronavirus infections.
Keywords: ARE-binding proteins; MK2 kinase; MKK3 kinase; ZFP36; coronavirus; p38 MAPK; proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

