FGF1 and insulin control lipolysis by convergent pathways
- PMID: 34986332
- PMCID: PMC8863067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.004
FGF1 and insulin control lipolysis by convergent pathways
Abstract
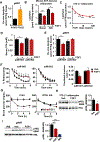
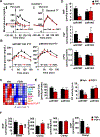
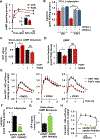
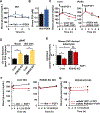
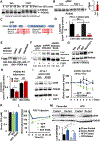
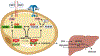
Inexorable increases in insulin resistance, lipolysis, and hepatic glucose production (HGP) are hallmarks of type 2 diabetes. Previously, we showed that peripheral delivery of exogenous fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) has robust anti-diabetic effects mediated by the adipose FGF receptor (FGFR) 1. However, its mechanism of action is not known. Here, we report that FGF1 acutely lowers HGP by suppressing adipose lipolysis. On a molecular level, FGF1 inhibits the cAMP-protein kinase A axis by activating phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), which separates it mechanistically from the inhibitory actions of insulin via PDE3B. We identify Ser44 as an FGF1-induced regulatory phosphorylation site in PDE4D that is modulated by the feed-fast cycle. These findings establish the FGF1/PDE4 pathway as an alternate regulator of the adipose-HGP axis and identify FGF1 as an unrecognized regulator of fatty acid homeostasis.
Keywords: FGF1; PDE4; cAMP; hepatic glucose production; insulin; lipolysis; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.R.A., R.T.Y., M.D., and R.M.E. are co-inventors of mutated FGF1 proteins and methods of use and may be entitled to royalties.
Figures
Comment in
-
FGF1 signalling cascade suppresses lipolysis.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022 Mar;18(3):135. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00634-1. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35046569 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmad F, Lindh R, Tang Y, Ruishalme I, Ost A, Sahachartsiri B, Strålfors P, Degerman E, and Manganiello VC (2009). Differential regulation of adipocyte PDE3B in distinct membrane compartments by insulin and the beta3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL316243: effects of caveolin-1 knockdown on formation/maintenance of macromolecular signalling complexes. Biochem J 424, 399–410. 10.1042/BJ20090842. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

