Increased Risk of Liver-Related Outcomes in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34986486
- PMCID: PMC9808743
- DOI: 10.1159/000521768
Increased Risk of Liver-Related Outcomes in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients with metabolic syndrome (MetS) may present increased risk of liver-related outcomes (LROs), but prior studies were limited by small sample size and/or conflicting results. Using a systematic review and meta-analytic approach, we aimed to determine the association between MetS and LROs in CHB.
Methods: Two researchers independently screened studies from the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases from inception to January 21, 2020, and extracted the data. Estimates were pooled using a random-effects model.
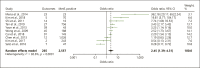
Results: We screened 2,228 articles and included 10 eligible studies (18,360 CHB patients, 2,557 with MetS). MetS was significantly associated with LROs overall (odds ratio = 2.45, 95% confidence interval = 1.39-4.32) but not the individual LRO components but subgroup analyses were limited by small study numbers.
Discussion/conclusion: MetS is associated with almost 3-folds higher risk of LROs in CHB and should be considered in management decisions. However, additional studies are needed.
Keywords: Diabetes; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver fibrosis; Mortality; Prognosis.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Mindie Nguyen has served as a consultant or in advisory board for Spring Bank, Novartis, Gilead, Intercept, Exact Sciences, Laboratory of Advanced Medicine, Eisai, and Bayer and has received grant/research support from Gilead, Pfizer, Enanta, Vir, National Cancer Institute, B. K. Kee Foundation, and Glycotest. All others: none to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Schweitzer A, Horn J, Mikolajczyk RT, Krause G, Ott JJ. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet. 2015;386((10003)):1546–1555. - PubMed
-
- Lai CL, Ratziu V, Yuen MF, Poynard T. Viral hepatitis B. Lancet. 2003 Dec;362((9401)):2089–2094. - PubMed
-
- McMahon BJ. Epidemiology and natural history of hepatitis B. Semin Liver Dis. 2005;25(Suppl 1):3–8. - PubMed
-
- Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet. 2013;381((9865)):468–475. - PubMed
-
- Chen CL, Yang HI, Yang WS, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, You SL, et al. Metabolic factors and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma by chronic hepatitis B/C infection: a follow-up study in Taiwan. Gastroenterology. 2008;135((1)):111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical