Risk prediction in patients with low-flow, low-gradient aortic stenosis and reduced ejection fraction undergoing TAVI
- PMID: 34987075
- PMCID: PMC8734034
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2021-001912
Risk prediction in patients with low-flow, low-gradient aortic stenosis and reduced ejection fraction undergoing TAVI
Abstract
Objective: Patients with low-flow, low-gradient aortic stenosis (LFLG AS) and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are known to suffer from poor prognosis after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). This study aimed to develop a simple score system for risk prediction in this vulnerable subset of patients.
Methods: All patients with LFLG AS with reduced EF and sufficient CT data for aortic valve calcification (AVC) quantification, who underwent TAVI at five German centres, were retrospectively included. The Risk prEdiction in patients with Low Ejection Fraction low gradient aortic stenosis undergoing TAVI (RELiEF TAVI) score was developed based on multivariable Cox regression for all-cause mortality.
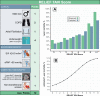
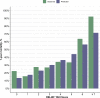
Results: Among all included patients (n=718), RELiEF TAVI score variables were defined as independent predictors of mortality: male sex (HR 1.34 (1.06, 1.68), p=0.013), underweight (HR 3.10 (1.50, 6.40), p=0.0022), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (HR 1.55 (1.21, 1.99), p=0.001), pulmonary hypertension (HR 1.51 (1.17, 1.94), p=0.0015), atrial fibrillation (HR 1.28 (1.03, 1.60), p=0.028), stroke volume index (HR 0.96 (0.95, 0.98), p<0.001), non-transfemoral access (HR 1.36 (1.05, 1.76), p=0.021) and low AVC density (HR 1.44 (1.15, 1.79), p=0.0012). A score system was developed ranging from 0 to 12 points (risk of 1-year mortality: 13%-99%). Kaplan-Meier analysis for low (0-1 points), moderate (2-4 points) and high RELiEF TAVI score (>4 points) demonstrated rates of 18.0%, 29.0% and 46.1% (p<0.001) for all-cause mortality and 23.8%, 35.9% and 53.4% (p<0.001) for the combined endpoint of all-cause mortality or heart failure rehospitalisation after 1 year, respectively.
Conclusions: The RELiEF TAVI score is based on simple clinical, echocardiographic and CT parameters and might serve as a helpful tool for risk prediction in patients with LFLG AS and reduced LVEF scheduled for TAVI.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; echocardiography; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SL reports non-financial support from Edwards Lifesciences. MS reports non-financial support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Nicolai Medizintechnik, OrbusNeich Medical, personal fees from Abiomed, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Philips and Shockwave Medical, grants from Philips. DW reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Berlin-Chemie and Novartis. J-MS is proctor for Medtronic and Boston Scientific, received research grants and speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic and Boston Scientific. DF is consultant for Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic and received research funding from Edwards Lifesciences. TR received speaker honoraria from Boston Scientific, Edwards, Medtronic, Abbott. LC is proctor and consultant for Edwards Lifesciences and Boston Scientific and consultant for Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. NS reports personal fees from Boston Scientific and non-financial support from Abbott and Edwards Lifesciences.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Outcomes From Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Low-Flow, Low-Gradient Aortic Stenosis and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Less Than 30%: A Substudy From the TOPAS-TAVI Registry.JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jan 1;4(1):64-70. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.4320. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30566185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of atrial fibrillation with survival in patients with low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis with preserved ejection fraction undergoing TAVI.Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2024 May 22;10(3):246-255. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcad045. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 37491693
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Low-Flow, Low-Gradient Aortic Stenosis: The TOPAS-TAVI Registry.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Mar 27;71(12):1297-1308. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.01.054. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29566812
-
Meta-Analysis of the Prognostic Impact of Stroke Volume, Gradient, and Ejection Fraction After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation.Am J Cardiol. 2015 Sep 15;116(6):989-94. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.06.027. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Am J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26195275 Review.
-
Optimal Threshold of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction for Aortic Valve Replacement in Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Apr 6;10(7):e020252. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020252. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33787311 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Reduced Ejection Fraction and Nonsevere Aortic Stenosis.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2023 May;16(5):e012768. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.122.012768. Epub 2023 May 16. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2023. PMID: 37192310 Free PMC article.
-
[Interventional treatment of heart failure : Stents and valves].Herz. 2023 Mar;48(2):101-108. doi: 10.1007/s00059-022-05160-4. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Herz. 2023. PMID: 36700948 Review. German.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
