Janus kinase-targeting therapies in rheumatology: a mechanisms-based approach
- PMID: 34987201
- PMCID: PMC8730299
- DOI: 10.1038/s41584-021-00726-8
Janus kinase-targeting therapies in rheumatology: a mechanisms-based approach
Abstract
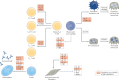
The four Janus kinase (JAK) proteins and seven signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) transcription factors mediate intracellular signal transduction downstream of cytokine receptors, which are implicated in the pathology of autoimmune, allergic and inflammatory diseases. Development of targeted small-molecule therapies such as JAK inhibitors, which have varied selective inhibitory profiles, has enabled a paradigm shift in the treatment of diverse disorders. JAK inhibitors suppress intracellular signalling mediated by multiple cytokines involved in the pathological processes of rheumatoid arthritis and many other immune and inflammatory diseases, and therefore have the capacity to target multiple aspects of those diseases. In addition to rheumatoid arthritis, JAK inhibition has potential for treatment of autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and alopecia areata, in which stimulation of innate immunity activates adaptive immunity, leading to generation of autoreactive T cells and activation and differentiation of B cells. JAK inhibitors are also effective in the treatment of allergic disorders, such as atopic dermatitis, and can even be used for the COVID-19-related cytokine storm. Mechanism-based treatments targeting JAK-STAT pathways have the potential to provide positive outcomes by minimizing the use of glucocorticoids and/or non-specific immunosuppressants in the treatment of systemic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.T. has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Mitsubishi-Tanabe and YL Biologics, and received research grants from Abbvie, Asahi-Kasei, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Corrona, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Kowa, Mitsubishi-Tanabe and Takeda, and consultant fees from AbbVie, Ayumi, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi and Taisho. S.N. has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from Asahi-kasei, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer and Sanofi, and has received research grants from Mitsubishi-Tanabe and Novartis. J.J.O. declares receipt of US patent royalties related to JAK inhibitors and NIH Cooperative Research and Development Agreement with Pfizer. Y.M.L. declares no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Smolen JS, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018;8:18001. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020;79:685–699. - PubMed
-
- Macchi P, et al. Mutations of Jak-3 gene in patients with autosomal severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) Nature. 1995;377:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Johnston JA, et al. Phosphorylation and activation of the Jak-3 Janus kinase in response to interleukin-2. Nature. 1994;370:151–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

