Research challenges and opportunities in the Caribbean area: first bibliometric study in the French West Indies, from 1989 to 2018
- PMID: 34987279
- PMCID: PMC8699030
- DOI: 10.26633/RPSP.2021.159
Research challenges and opportunities in the Caribbean area: first bibliometric study in the French West Indies, from 1989 to 2018
Abstract
Objective: To analyze, describe, and quantify the collaborations and scientific output of the two university teaching hospitals of Martinique and Guadeloupe, at the regional, national, and international level.
Methods: A bibliometrics analysis was performed from the international databases Web of Science and PubMed, for the period from 1989 to 2018, inclusive (30 years). Three types of bibliometric indicators were used, namely quantitative indicators, performance indicators, and organization-specific indicators. Affiliations of the first and last authors were identified from PubMed.
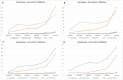
Results: Between 1989 and 2018, a total of 1 522 indexed articles were published with at least one author affiliated to either the University Hospital of Martinique (n = 827) or the University Hospital of Guadeloupe (n = 685). The majority of articles were in category Q1 (35.8% for Martinique and 35.2% for Guadeloupe). In Martinique, over the last 30 years, the three main research areas have been clinical neurology, ophthalmology, and surgery, together representing 28.7% of all research areas, with the highest number of articles published in the field of clinical neurology (n = 81). In the University Hospital of Guadeloupe, the area of hematology was largely represented, with 79 articles published. For both hospitals, the first and last authors of the articles published were mainly from mainland France.
Conclusions: This quantitative analysis shows the development of medical and scientific research in Martinique and Guadeloupe over the last three decades, as well as the extent of their collaborative partnerships at the national and international levels.
Objetivo: Analizar, describir y cuantificar las colaboraciones y la producción científica de los dos hospitales docentes universitarios de Martinica y Guadalupe, al nivel regional, nacional e internacional.
Métodos: Se llevó a cabo un análisis de bibliometría de las bases de datos internacionales Web of Science y PubMed, en el período de 1989 al 2018, inclusive (30 años). Se emplearon tres tipos de indicadores bibliométricos, a saber: indicadores cuantitativos, indicadores de rendimiento e indicadores específicos de organización. Se establecieron las afiliaciones de los primeros y últimos autores de PubMed.
Resultados: Entre 1989 y el 2018, se publicaron en total 1 522 artículos indizados con al menos un autor afiliado al Hospital Universitario de Martinica (n = 827) o bien al Hospital Universitario de Guadalupe (n = 685). La mayoría de los artículos estaban en el cuartil 1 (35,8 % en Martinica y 35,2 % en Guadalupe). En Martinica, en los últimos 30 años las tres principales áreas de investigación han sido la neurología clínica, la oftalmología y la cirugía, que juntas representan 28,7 % de todas las áreas de investigación, con el número más alto de artículos publicado en el campo de la neurología clínica (n = 81). En el Hospital Universitario de Guadalupe, el ámbito de la hematología estaba ampliamente representado, con 79 artículos publicados. En ambos hospitales, los primeros y los últimos autores de los artículos publicados eran principalmente de Francia continental.
Conclusiones: Este análisis cuantitativo demuestra el desarrollo de la investigación médica y científica en Martinica y Guadalupe en los treinta últimos años, así como el alcance de sus asociaciones colaborativas a los niveles nacional e internacional.
Objetivo: Analisar, descrever e quantificar as colaborações e a produção científica dos dois hospitais universitários de Martinica e Guadalupe, no âmbito regional, nacional e internacional.
Métodos: Foi realizada uma análise bibliométrica das bases de dados internacionais Web of Science e PubMed, no período de 1989 a 2018, inclusive (30 anos). Três tipos de indicadores bibliométricos foram utilizados: quantitativos, de desempenho e específicos da organização. Afiliações dos primeiros e últimos autores foram identificadas na base PubMed.
Resultados: Entre 1989 e 2018, um total de 1 522 artigos indexados foram publicados com pelo menos um autor afiliado ao Hospital Universitário de Martinica (n = 827) ou ao Hospital Universitário de Guadalupe (n = 685). A maioria dos artigos estava na categoria Q1 (35,8% para Martinica e 35,2% para Guadalupe). Na Martinica, nos últimos 30 anos, as três principais áreas de pesquisa foram neurologia clínica, oftalmologia e cirurgia, representando, juntas, 28,7% de todas as áreas de pesquisa, com o maior número de artigos publicados no campo da neurologia clínica (n = 81). No Hospital Universitário de Guadalupe, a área de hematologia foi amplamente representada, com 79 artigos publicados. Para ambos os hospitais, os primeiros e os últimos autores dos artigos publicados eram principalmente da França continental.
Conclusões: Esta análise quantitativa demonstra o desenvolvimento da pesquisa médica e científica na Martinica e em Guadalupe nas três últimas décadas, bem como a extensão de suas parcerias colaborativas no âmbito nacional e internacional.
Keywords: Caribbean region; Collaboration indicator; Guadeloupe; Martinique; bibliometrics.
Figures
References
-
- Pritchard A. Statistical Bibliography or Bibliometrics. J Doc. 1969;25:348–349.
- Pritchard A. Statistical Bibliography or Bibliometrics? J Doc. 1969;25:348–9.
-
- Devos P, Menard J. Bibliometric analysis of research relating to hypertension reported over the period 1997–2016. J Hypertens. 2019;37(11):2116–2122. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002143. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Devos P, Menard J. Bibliometric analysis of research relating to hypertension reported over the period 1997–2016. J Hypertens. 2019;37(11):2116–22. 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002143 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baudoin L, Akiki V, Magnan A, Devos P. Publication output of French university hospitals during 2006-2015: Trends and position in the national health research landscape. Presse Med. 2018;47(11-12 Pt 1):e175–e186. - PubMed
- Baudoin L, Akiki V, Magnan A, Devos P. [Publication output of French university hospitals during 2006-2015: Trends and position in the national health research landscape]. Presse Med. 2018;47(11-12 Pt 1):e175–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources